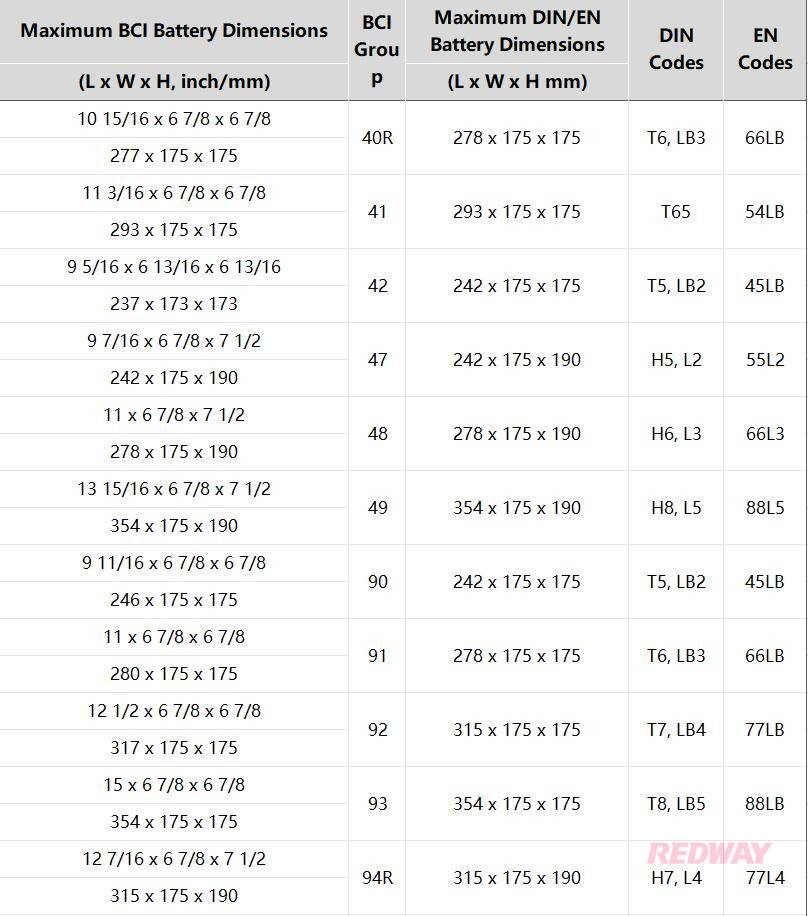
A battery cross reference chart helps riders easily find compatible batteries for powersports, ATVs, and motorcycles by matching sizes, cold cranking amps (CCA), and terminals. It simplifies choosing the right lithium or lead-acid battery, ensuring optimal performance and longevity across brands and models.
How Does a Battery Cross Reference Chart Simplify Choosing Powersports Batteries?
A battery cross reference chart matches batteries’ physical dimensions, terminal types, and electrical specs, simplifying the selection process for powersports vehicles. It helps users identify equivalent batteries across brands, preventing compatibility issues and ensuring reliable starts.
Battery compatibility depends on size group, CCA rating, voltage, and terminal layout. Charts consolidate this info, allowing riders to swap out brands or upgrade technologies without guessing. For example, an AGM battery can replace a flooded type if specifications match. This tool reduces trial and error, saves money, and boosts confidence in battery maintenance.
What Are the Key Specifications to Compare in ATVs and Motorcycle Batteries?
The key specs include battery group size, voltage (usually 12V), CCA, reserve capacity, and terminal position. These ensure fit and enough power to start engines, especially in cold conditions.
Group size dictates physical fit in the battery compartment. Voltage must match vehicle requirements. Cold cranking amps measure starting power—critical for engines exposed to cold. Terminal type/placement affect cable connections. Reserve capacity indicates how long the battery can power the system if the alternator fails. Matching these specs maintains engine reliability and battery lifespan.
Which Battery Types Are Best for Powersports, ATVs, and Motorcycles?
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) and sealed Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) batteries are increasingly preferred due to low maintenance, high performance, and long life. Conventional flooded lead-acid batteries are still common but less durable.
LiFePO4 batteries from manufacturers like Redway Battery provide lightweight, stable power with faster recharging and deeper discharge capabilities. AGM batteries offer good vibration resistance and leak-proof design, ideal for rough terrains. Choosing the right chemistry depends on budget, performance needs, and maintenance preferences.
Why Is It Important to Consider Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) in Battery Selection?
CCA rating indicates the battery’s ability to provide sufficient power to start the engine at low temperatures. Selecting a battery with inadequate CCA can lead to starting failures in cold weather.
Powersports vehicles often operate outdoors in variable climates. A high CCA ensures the battery delivers enough current for quick starts under stress. Using a cross reference chart helps confirm replacement batteries meet or exceed the original CCA specifications, ensuring reliable operation year-round.
Where Can Riders Find Reliable Battery Cross Reference Charts?
Reliable battery cross reference charts are available from battery manufacturers, specialized retail sites, and OEM service guides. Brands like Redway Battery publish detailed cross references to assist customers in selecting compatible lithium and lead-acid batteries.
Authorized dealers and well-known powersports forums often host interactive charts. Some retailers provide app-based tools enabling users to enter vehicle info and get instant compatible battery matches. Checking multiple sources and official manufacturer charts ensures accuracy and reliability.
How Can Riders Maintain Lithium Batteries for Powersports and Motorcycles?
Proper maintenance includes keeping batteries clean, charged, and stored in a cool, dry place. Regular voltage checks and avoiding deep discharges extend lithium battery life.
Unlike flooded batteries, lithium packs like those from Redway Battery require minimal maintenance but benefit from periodic balance charging. Avoid extreme temperatures and vibrations, use compatible chargers, and disconnect during long inactivity. Following manufacturer instructions helps maximize lifespan and performance.
Does Using a Lithium Battery Affect Vehicle Performance?
Yes, lithium batteries often improve vehicle performance by reducing weight, providing consistent voltage, and enhancing cold-weather starts. They also have longer cycle life compared to traditional lead-acid types.
Lightweight lithium batteries contribute to better handling and fuel efficiency. Their ability to sustain voltage under load delivers stable electrical output for lights and electronics. Rapid recharge capability reduces downtime. These performance benefits make lithium an attractive upgrade for powersports and motorcycle enthusiasts.
What Are Common Battery Group Sizes for Powersports, ATVs, and Motorcycles?
Common group sizes include 24, 30, 34, 35, YTX7L, and YTX9L, among others. These denote standardized dimensions and terminal layouts ensuring fitment.
For example, YTX7L is typical for many small motorcycles and ATVs, while Group 24 or 30 batteries suit larger powersports vehicles. Cross reference charts detail which brands and models share these sizes, helping users find exact or equivalent replacements.
Who Should Consider Customized Battery Solutions for Powersports Vehicles?
Riders or fleet operators using specialized equipment or devices requiring precise power delivery should consider custom battery solutions. Redway Battery offers OEM/ODM customization for unique voltage, capacity, or form factor needs.
Customized packs can optimize space utilization, improve thermal management, and integrate better with vehicle electronics. Fleets or aftermarket modifiers seeking high reliability and performance gain advantages from tailored battery designs meeting exact application demands.
When Is the Best Time to Replace a Powersports Battery?
Replace batteries when they show signs of failure such as slow cranking, dim lights, or frequent recharge needs, typically every 3-5 years. Lithium batteries may last longer but still degrade over time.
Seasonal maintenance or pre-ride checks are ideal to gauge battery health. Using a cross reference chart before replacement ensures correct fit and specs. Upgrading to lithium models during replacement can provide immediate performance benefits.
Redway Expert Views
“Selecting the right battery goes beyond matching physical size; it’s about understanding the chemistry, power demands, and lifestyle of powersports enthusiasts,” explains the engineering team at Redway Battery. “Our focus on high-quality LiFePO4 batteries ensures durable, safe, and customizable power solutions that enhance rider experience and reduce downtime. Riders seeking reliability trust Redway not only for product performance but also for our commitment to innovation and service excellence.”
Conclusion
Understanding how to use a battery cross reference chart for powersports, ATVs, and motorcycles simplifies selecting the right replacement battery. Paying attention to specifications like group size, CCA, and chemistry ensures compatibility and performance. Lithium batteries, such as those from Redway Battery, offer superior longevity and reliability. Proper maintenance and timely replacement further safeguard your vehicle’s operation. Always consult reliable charts and trusted manufacturers like Redway Battery for the best battery solutions.
FAQs
Q1: Can I replace a lead-acid battery with a lithium battery in my ATV?
Yes, if the lithium battery matches the voltage, size, and terminal configuration, it can be a superior replacement offering better performance and lifespan.
Q2: How often should I check my powersports battery’s health?
Check at least once per riding season or every 3-6 months to avoid unexpected failures.
Q3: Does using a cross reference chart guarantee perfect battery fit?
It significantly reduces errors but verifying physical dimensions and terminal positions before purchase is recommended.
Q4: Are lithium batteries safe for extreme weather?
Yes, especially LiFePO4 types, which handle temperature extremes better than traditional lead-acid batteries.
Q5: Where can I buy Redway Battery products?
Redway Battery products are available worldwide via authorized distributors and OEM partnerships ensuring quality and warranty support.