Lithium-ion batteries self-discharge after being fully charged due to internal chemical reactions, environmental factors, and other factors. This self-discharge can reduce the battery’s capacity and performance and may lead to early battery failure.
-
Internal Chemical Reactions:
Lithium-ion batteries contain various components, including electrodes and electrolytes. Over time, internal chemical reactions can occur within the battery, leading to self-discharge. These reactions can cause the gradual loss of stored energy, reducing the battery’s capacity and overall performance. -
Environmental Factors:
Environmental factors, such as temperature, can also contribute to self-discharge in lithium-ion batteries. High temperatures can accelerate the self-discharge process, causing the battery to lose energy more quickly. Conversely, storing the battery in low temperatures can slow down the self-discharge rate. -
Impact on Battery Performance:
Self-discharge in lithium-ion batteries can have significant implications for their performance. As the battery loses stored energy over time, its capacity decreases, resulting in reduced runtime and overall efficiency. Additionally, self-discharge can lead to early battery failure if not properly managed.
What is a Lithium-Ion Battery?
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible intercalation of Li⁺ ions into electronically conducting solids to store energy. These batteries consist of single or multiple lithium-ion cells, along with a protective circuit board. They are widely used in various electronic devices due to their high energy density and long cycle life.
-
Rechargeable and Intercalation:
A lithium-ion battery is a rechargeable battery that stores and releases energy through the reversible intercalation of Li⁺ ions into electronically conducting solids. This intercalation process allows the battery to efficiently store and deliver electrical energy, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. -
Composition and Structure:
Lithium-ion batteries consist of one or multiple lithium-ion cells, which contain positive and negative electrodes separated by a separator. The electrodes are typically made of materials that can intercalate lithium ions, enabling the reversible movement of ions during charge and discharge cycles. Additionally, a protective circuit board ensures the safe and optimal operation of the battery. -
Advantages and Applications:
Lithium-ion batteries offer several advantages, including high energy density, long cycle life, and relatively low self-discharge rate. These characteristics make them ideal for powering portable electronic devices such as smartphones, laptops, tablets, and electric vehicles. The ability to recharge and reuse lithium-ion batteries contributes to reducing environmental waste and promoting sustainable energy solutions.
Causes of Self-Discharge
Causes of self-discharge in lithium-ion batteries include moisture, internal chemical reactions, and environmental factors. These factors can gradually reduce the battery’s capacity and performance, impacting its overall efficiency.
-
Moisture:
Moisture is one of the primary causes of self-discharge in lithium-ion batteries. Over time, the electrolyte solvent or water within the battery can get dissolved, leading to a gradual loss of stored energy. It is important to store lithium-ion batteries in dry environments to minimize the impact of moisture on self-discharge. -
Internal Chemical Reactions:
Internal chemical reactions within the battery can also contribute to self-discharge. These reactions can occur even when the battery is not in use, gradually reducing its stored charge. Factors such as the composition of the battery’s electrodes and the presence of impurities can influence the rate of self-discharge. -
Environmental Factors:
Environmental factors, such as temperature, can significantly impact self-discharge in lithium-ion batteries. High temperatures can accelerate self-discharge, causing the battery to lose energy more quickly. Conversely, storing the battery at lower temperatures can slow down the self-discharge rate. It is important to consider the recommended temperature range for storing and using lithium-ion batteries to minimize self-discharge.
Temperature’s Role in Self-Discharge
Factors that impact self-discharge in lithium-ion batteries include high temperatures and excessive humidity, both of which increase the rate of electrolyte breakdown. Excessive temperatures can also cause the deterioration of the solid electrolyte interface (SEI), leading to increased self-discharge and loss of lithium.
-
Impact of High Temperatures:
High temperatures can accelerate self-discharge in lithium-ion batteries. When exposed to excessive heat, the rate of electrolyte breakdown increases, leading to a higher self-discharge rate. This can result in the loss of stored energy and reduced battery capacity over time. Additionally, high temperatures can cause the deterioration of the solid electrolyte interface (SEI), further contributing to self-discharge and the loss of lithium. -
Preservation of Solid Electrolyte Interface (SEI):
The solid electrolyte interface (SEI) is a protective layer that forms on the surface of lithium-ion battery electrodes. It acts as a barrier, preventing the unwanted reactions between the electrolyte and the electrodes. However, high temperatures can compromise the integrity of the SEI, reducing its effectiveness and allowing for increased self-discharge. -
Optimal Storage Conditions:
To minimize self-discharge and preserve the performance of lithium-ion batteries, it is crucial to store them within the recommended temperature range. Ideally, temperatures between 15°C to 25°C (59°F to 77°F) provide optimal conditions for minimizing self-discharge. By maintaining suitable storage temperatures, users can mitigate the negative effects of temperature on self-discharge and ensure the longevity of their lithium-ion batteries.
Mitigating Self-Discharge
Mitigating self-discharge in batteries is essential for preserving their performance and longevity. Methods to minimize self-discharge include optimizing electrolytes, modifying electrode materials, controlling temperature and humidity conditions, and implementing effective battery management systems. By mitigating self-discharge, batteries can retain their stored energy for longer periods, ensuring reliable power availability.
-
Optimizing Electrolytes and Electrode Materials:
One approach to mitigate self-discharge is by optimizing the composition and properties of electrolytes and electrode materials. Researchers have been exploring the use of additives and surface modifications to enhance the stability and reduce the self-discharge rate of batteries. By carefully selecting and designing these components, it is possible to minimize self-discharge and improve overall battery performance. -
Controlling Temperature and Humidity:
Temperature and humidity conditions can significantly impact self-discharge in batteries. High temperatures and excessive humidity can accelerate self-discharge rates, leading to energy loss and reduced battery capacity. Implementing proper temperature and humidity control measures, such as thermal management systems and moisture-resistant packaging, can help mitigate self-discharge and preserve battery performance. -
Effective Battery Management Systems:
Implementing effective battery management systems is another key aspect of mitigating self-discharge. These systems monitor and control various parameters such as voltage, temperature, and state of charge to optimize battery performance and minimize self-discharge. By implementing intelligent charging and discharging algorithms, battery management systems can ensure efficient energy utilization and reduce self-discharge.
Preventing Self-Discharge
To prevent self-discharge in batteries, store them in a cool, dry place and avoid contact with metal. Storing batteries at lower temperatures reduces the rate of self-discharge and helps preserve the initial energy stored in the battery.
-
Storing Batteries at Lower Temperatures:
Self-discharge is a chemical reaction that occurs more quickly at higher temperatures. By storing batteries in a cool, dry place, such as a refrigerator or a temperature-controlled environment, the rate of self-discharge can be reduced. Lower temperatures help preserve the initial energy stored in the battery, ensuring it remains available for longer periods. -
Avoiding Contact with Metal:
Another way to prevent self-discharge is by avoiding contact between batteries and metal objects. Metal can create a conductive path that allows self-discharge to occur more rapidly. To minimize self-discharge, it is advisable to store batteries in their original packaging or in non-conductive containers, away from metal objects.
Preventing self-discharge in batteries is essential for maintaining their energy storage capacity. Storing batteries at lower temperatures and avoiding contact with metal are effective methods to minimize self-discharge. By implementing these preventive measures, users can ensure that their batteries retain their stored energy for longer periods, providing reliable power when needed. Remember to store batteries in cool, dry places and keep them away from metal objects to prevent self-discharge and optimize battery performance.
Considerations and Downsides
Impact on Battery Lifespan
Constantly maintaining batteries at full charge can stress internal components and reduce overall capacity over time.
Risk of Overcharging
Continuous full charge can bypass protective circuits, potentially compromising battery safety.
Long-Term Performance
Balancing between storage conditions and usage frequency is crucial for maximizing battery longevity and performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while lithium-ion batteries offer unparalleled efficiency, self-discharge remains a challenge. By understanding its causes and implementing proactive measures like optimal storage and smart charging, you can extend battery life and enhance device performance. For more insights and expert advice on battery management, reach out to us today.
FAQs
What causes batteries to self-discharge?
Self-discharge is a phenomenon in batteries where internal chemical reactions reduce the stored charge of the battery without any connection between the electrodes or any external circuit. Factors such as age, cycling, elevated temperature, and the solubility of the positive electrode material in the electrolyte can impact the rate of self-discharge.
-
Internal Chemical Reactions:
Self-discharge in batteries is a result of internal chemical reactions that occur within the battery, leading to the reduction of stored charge. These reactions can take place even when the battery is not connected to any external circuit. The exact mechanisms of these reactions can vary depending on the type of battery and its composition. -
Factors Affecting Self-Discharge:
Several factors can influence the rate of self-discharge in batteries. Age, cycling (charge-discharge cycles), and elevated temperatures can accelerate self-discharge. Additionally, the solubility of the positive electrode material in the electrolyte can also impact the rate of self-discharge. Understanding these factors helps in implementing strategies to minimize self-discharge and preserve battery capacity. -
Impact of Temperature:
Temperature plays a significant role in the rate of self-discharge. Higher temperatures can accelerate the internal chemical reactions, leading to a faster reduction in the stored charge. It is important to store batteries in cool environments to minimize self-discharge and preserve their energy storage capacity.
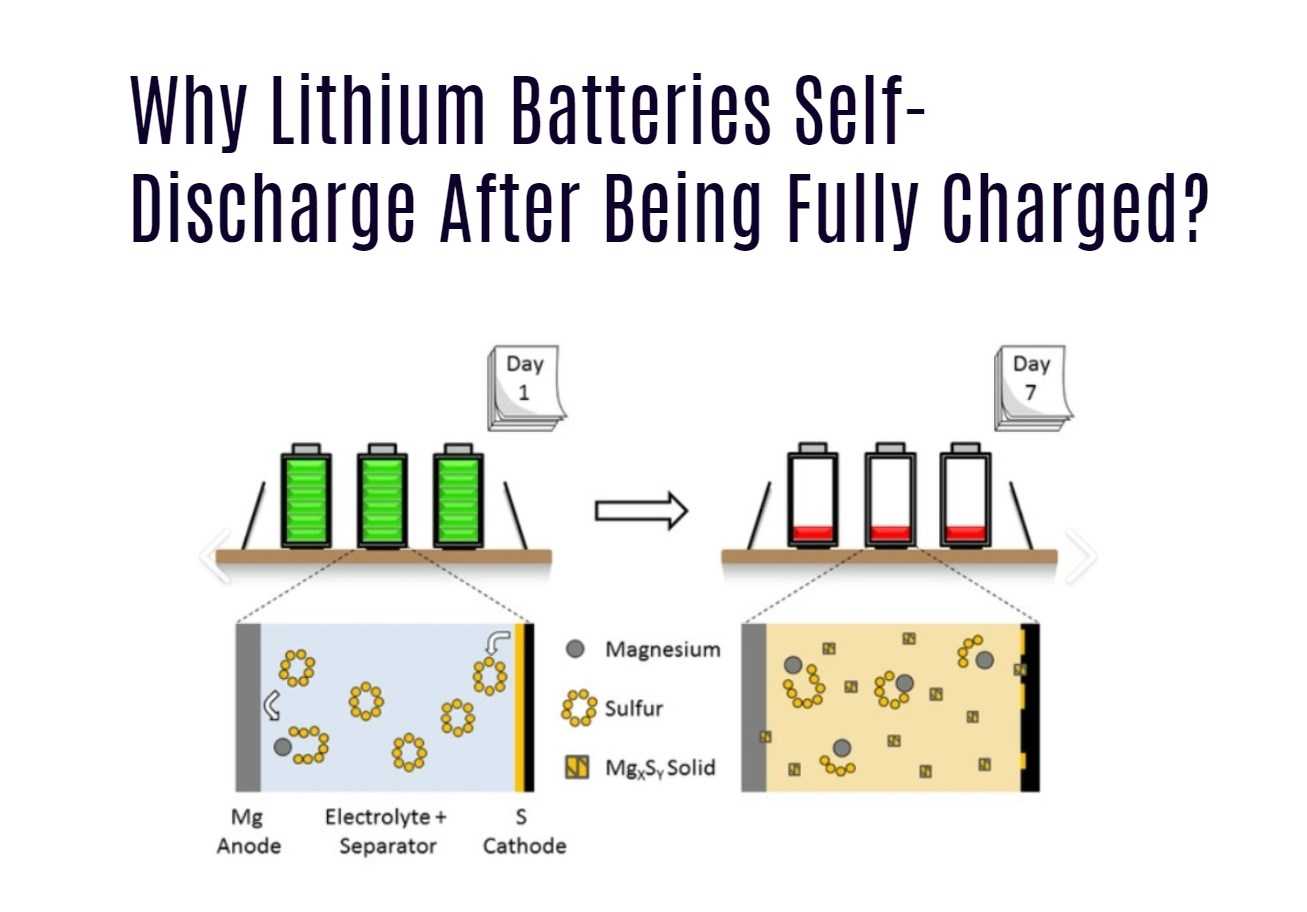
Does temperature affect how quickly a battery will self-discharge?
Yes, temperature affects the rate of self-discharge in batteries. Self-discharge tends to occur more quickly at higher temperatures. Storing batteries at lower temperatures can help slow down the rate of self-discharge and preserve the battery’s energy storage capacity.
-
Accelerated Self-Discharge at Higher Temperatures:
Higher temperatures can accelerate the chemical reactions responsible for self-discharge in batteries. The increased thermal energy provides more energy for these reactions to occur, leading to a faster reduction in the stored charge of the battery. This phenomenon is particularly evident in certain battery chemistries, such as lead-acid and nickel-metal hydride batteries. -
Slowing Down Self-Discharge with Lower Temperatures:
Storing batteries at lower temperatures can help slow down the rate of self-discharge. Cooler temperatures reduce the thermal energy available for the self-discharge reactions, effectively preserving the battery’s energy storage capacity for longer periods. This is why it is recommended to store batteries in cool environments, especially when they are not in use for extended periods. -
Balancing Temperature for Optimal Performance:
While lower temperatures can slow down self-discharge, extremely low temperatures can also affect battery performance. Very cold temperatures can increase the internal resistance of the battery, reducing its ability to deliver power effectively. Therefore, it is important to strike a balance and avoid exposing batteries to extreme temperatures to maintain optimal performance.
How can you prevent or slow down self-discharge?
To prevent or slow down self-discharge in batteries, ensure that the battery terminals are clean and tight, maintain the proper electrolyte level, store batteries in the right conditions, and avoid extreme temperatures. These methods help minimize the chemical reactions responsible for self-discharge and preserve the battery’s energy storage capacity.
-
Clean and Tight Battery Terminals:
Ensuring that the battery terminals are clean and tight is important to prevent self-discharge. Dirty or corroded terminals can create resistance and lead to unnecessary discharge. Regularly inspect and clean the terminals, removing any dirt or corrosion, and ensure a secure connection between the battery and the device. -
Maintain Proper Electrolyte Level:
For batteries that require electrolyte, such as lead-acid batteries, it is essential to maintain the proper electrolyte level. Low electrolyte levels can lead to increased self-discharge. Regularly check the electrolyte level and add distilled water if necessary, following the manufacturer‘s guidelines. -
Store Batteries in the Right Conditions:
Proper storage conditions can significantly impact self-discharge. Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. High temperatures accelerate self-discharge, while extreme cold can affect battery performance. Storing batteries in their original packaging or in non-conductive containers can also help prevent self-discharge. -
Avoid Extreme Temperatures:
Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can accelerate self-discharge in batteries. It is important to avoid exposing batteries to temperature extremes, as this can lead to faster reduction in the stored charge. Optimal storage temperatures vary depending on the battery chemistry, so refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations.

Are there any downsides to preventing self-discharge?
No, there are no specific downsides to preventing self-discharge in batteries. Self-discharge is a natural process that occurs in all types of rechargeable batteries and cannot be completely eliminated. Managing self-discharge is important to preserve battery capacity.
-
Understanding Self-Discharge:
Self-discharge is a phenomenon that occurs in batteries over time, even when they are not in use. It is a natural process where the stored charge gradually decreases due to internal chemical reactions. Managing self-discharge is crucial for ensuring that batteries retain their capacity and are ready for use when needed. -
Importance of Managing Self-Discharge:
Preventing or slowing down self-discharge is important for preserving battery capacity. By minimizing self-discharge, batteries can retain their energy storage capacity for longer periods, ensuring reliable power availability. This is particularly crucial for applications where batteries are used intermittently or stored for extended periods. -
No Specific Downsides:
While managing self-discharge is important, there are no specific downsides associated with preventing it. Preventing self-discharge helps maintain the battery’s energy storage capacity and ensures that it is ready for use when needed. However, it is important to note that self-discharge is a natural process that cannot be completely eliminated. Therefore, it is necessary to strike a balance between preventing self-discharge and ensuring the battery remains functional.




