-
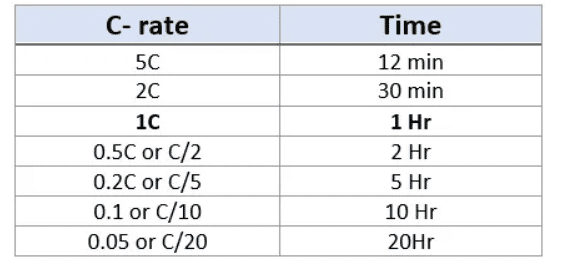
Definition of C-rate: The C-rate of a lithium battery indicates the discharge rate relative to its maximum capacity. It is expressed as a multiple of the battery’s rated capacity. For example, a C-rate of 1 means the battery can be fully discharged in 1 hour, while a C-rate of 2 indicates a discharge time of 30 minutes. The C-rate provides valuable information about the battery’s capabilities and limitations.
-
Calculation of C-rate: To calculate the C-rate of a lithium battery, divide the charge or discharge current by the rated capacity of the battery. For instance, if a battery has a rated capacity of 2,500 mAh and a discharge current of 5,000 mA, the C-rate would be 2C. This means the battery can be discharged at a rate twice its rated capacity. Understanding the C-rate helps in determining the suitable charging and discharging conditions for the battery.
-
Significance of C-rate: The C-rate plays a crucial role in battery performance and safety. Operating a battery beyond its recommended C-rate can lead to reduced capacity, increased internal resistance, and even thermal runaway. On the other hand, underutilizing the battery by operating at a lower C-rate than its capability may result in inefficient usage. Therefore, it is important to consider the C-rate when selecting and using lithium batteries to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
What is battery C rating?
-
Definition of Battery C Rating: The battery C rating is the measurement of current at which a battery is charged and discharged. It helps determine the battery’s capacity and performance, indicating how much current the battery can deliver or accept during charging and discharging processes.
-
The 1C Rate: The 1C rate is a common reference point in battery C rating. At the 1C rate, a fully charged battery should be able to deliver a current equal to its capacity for one hour. For example, a battery with a capacity of 10Ah rated at 1C can provide 10 Amps of current for one hour.
-
Multiple of Nominal Capacity: The C rating is typically expressed as a multiple of the battery’s nominal capacity. Higher C ratings indicate that the battery can deliver or accept higher currents, making it suitable for applications with higher power demands.
-
Importance of C Rating: The C rating is crucial for selecting a battery that can meet the specific power requirements of an application. It helps ensure that the battery can deliver the necessary current without being overloaded or underutilized. Understanding the C rating allows users to choose the right battery for their needs, balancing power requirements and battery capacity.
What are the effects of C rating on lithium-ion batteries?
-
Higher C Rating, More Power: The C rating of a battery determines its charge and discharge rate. A higher C rating indicates that the battery can supply more current and power, making it suitable for high-performance applications that require quick energy delivery. Batteries with higher C ratings are commonly used in electric vehicles, power tools, and other high-power applications.
-
Heat Generation and Battery Lifespan: While a higher C rating allows for greater power output, it can also lead to increased heat generation during high discharge rates. Excessive heat can impact the performance and lifespan of lithium-ion batteries. It is important to manage heat dissipation and ensure proper cooling to prevent damage to the battery.
-
Considerations for Specific Applications: The choice of C rating depends on the specific requirements of the application. Higher C ratings are beneficial for applications that demand high power output, but they may not be necessary for low-power devices. It is essential to consider the balance between power requirements and battery lifespan when selecting a lithium-ion battery with a specific C rating.
What is Battery Capacity?
-
Definition of Battery Capacity: Battery capacity refers to the total amount of electricity generated as a result of electrochemical reactions within the battery. It is commonly expressed in ampere hours (Ah) and represents the energy storage capacity of the battery. Battery capacity is a crucial parameter that determines how long a battery can power a device or system.
-
Calculation and Representation: Battery capacity is measured by the mass of the active material contained within the battery. It is typically denoted in units of watt-hours (Wh) or milliamp-hours (mAh). The capacity value indicates the amount of energy that the battery can store. For example, a battery with a capacity of 5 Ah can provide a continuous discharge current of 1 C (5 A) for 1 hour.
-
Importance of Battery Capacity: Understanding battery capacity is essential for evaluating the performance and efficiency of batteries. Higher battery capacity allows for longer operation times, while lower capacity may require more frequent recharging or replacement. Battery capacity also influences the power requirements of devices and systems, as higher-capacity batteries can deliver more energy to meet the demands of power-hungry applications.
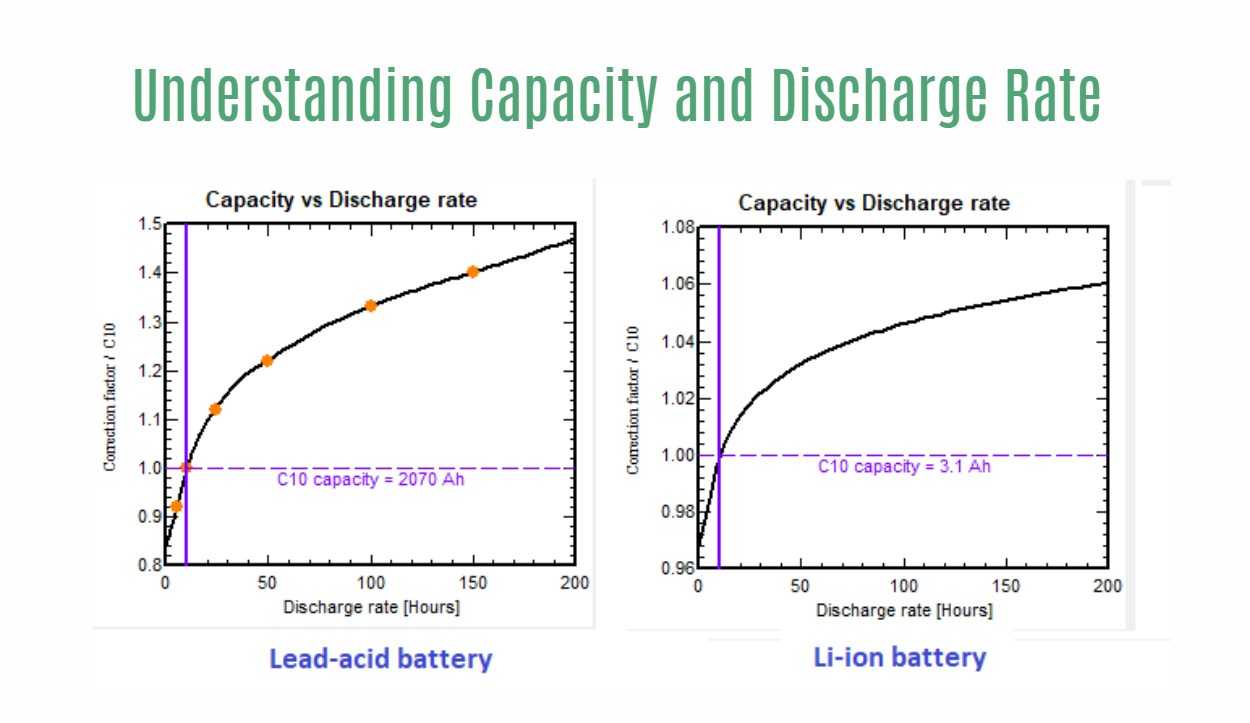
Understanding Capacity and Discharge Rate
-
Capacity Calculation: Battery capacity is calculated by multiplying the discharge current, measured in Amperes (A), by the discharge time, measured in hours (h). This calculation provides an estimation of the total charge that a battery can store. It is important to note that as the discharge rate increases, the capacity of the battery decreases. This means that batteries may not deliver their full capacity when discharged rapidly.
-
Nominal Capacity: For secondary batteries, the nominal capacity is often specified for specific discharge rates. This means that the capacity value provided is based on a particular discharge time, such as a 10-hour or 20-hour rate. The nominal capacity indicates the expected performance of the battery under those specific discharge conditions. It is essential to consider the discharge rate when comparing batteries for different applications.
-
Application Considerations: Understanding capacity and discharge rate is crucial for selecting batteries suitable for specific applications. Some applications may require batteries with high discharge rates to meet peak power demands, while others may prioritize longer discharge times and higher capacity for extended operation. By evaluating the capacity and discharge rate, users can choose batteries that align with their specific power requirements.
Impact of Discharge Rate on Capacity
-
Discharge Rate and Capacity: The discharge rate refers to the rate at which a battery is discharged, typically measured in Amperes (A). The capacity of a battery is commonly rated at a specific discharge rate, such as 1C. When a battery is discharged at a high rate, a large current is drawn quickly, which can result in a decrease in its effective capacity.
-
Factors Influencing Capacity Reduction: The reduction in capacity at high discharge rates is influenced by various factors. One of the primary factors is the change in chemical reactions occurring within the battery during rapid discharge. These changes can affect the efficiency of the electrochemical processes and limit the amount of charge that can be stored and delivered.
-
Impact of Internal Resistance: The internal resistance of a battery plays a significant role in determining its discharge rate capabilities. As the discharge rate increases, the internal resistance becomes more pronounced, leading to voltage drops and energy losses. The increased resistance contributes to a decrease in the effective capacity of the battery, as less energy can be efficiently delivered.
-
Optimizing Battery Performance: Understanding the impact of discharge rate on capacity is essential for optimizing battery performance. It helps in selecting batteries suitable for specific applications and determining the appropriate discharge conditions. By operating batteries within their recommended discharge rates, users can maximize their capacity utilization and prolong their overall lifespan.
Calculating Capacity at Different C-Rates
-
Calculation Method: To calculate the capacity at different C rates, multiply the nominal capacity of the battery by the specified C rate. The C rate represents the charge or discharge current relative to the maximum capacity of the battery. For instance, a 2000mAh battery at a 0.5C rate would provide an available current of 1A, while at a 2C rate, it would deliver 4A.
-
Evaluating Battery Performance: Understanding how to calculate capacity at different C rates is crucial for evaluating battery performance. It allows users to assess the battery’s ability to deliver the required current at varying discharge rates. By comparing the available current at different C rates, users can select batteries that meet their specific power requirements.
-
Application Considerations: Calculating capacity at different C rates helps in selecting batteries suitable for specific applications. Some applications may require batteries with higher C rates to meet peak power demands, while others may prioritize longer discharge times and higher capacity. By considering the calculated capacity at different C rates, users can choose batteries that align with their application requirements.
To calculate the C-rate of a battery, divide the current by the capacity of the battery. For example, if you have a 3 Ah battery and you discharge it at a current of 6A, the C-rate would be 2C (6A ÷ 3Ah).
C-rate is an important factor to consider when selecting a battery for a particular application. Choosing a battery with a higher C-rate will allow it to deliver more power and discharge more quickly, but may reduce the overall capacity and lifespan of the battery. Conversely, choosing a battery with a lower C-rate will provide a longer lifespan and more capacity, but may not be able to deliver as much power as quickly.
It’s important to note that the C-rate should be within the manufacturer’s specifications for the battery to avoid damaging the battery or reducing its lifespan.
Significance of Nominal Capacity and C-Rate
-
Nominal Capacity: Nominal capacity refers to the amount of charge a battery can deliver under specified conditions. It is often given for a specific discharge rate, such as a 10-hour or 20-hour rate. The nominal capacity provides an indication of the battery’s energy storage capability and is an important parameter for comparing batteries.
-
C-Rate: The C-rate is a measure of the rate at which a battery is discharged or charged relative to its maximum capacity. It is expressed as a multiple of the battery’s nominal capacity. For example, a 1C rate means discharging the battery in one hour, while a 0.5C rate means discharging it in two hours. The C-rate is used to express the discharge current and charging current of a battery.
-
Significance in Battery Selection: Understanding the nominal capacity and C-rate is crucial for selecting batteries suitable for specific applications. Different applications have different power requirements, and the discharge rate plays a significant role in meeting those requirements. By considering the nominal capacity and C-rate, users can choose batteries that align with their desired power needs and optimize the performance of their systems.
Practical Implications in Battery Selection
-
Primary vs. Secondary Batteries: One of the initial considerations in battery selection is deciding between primary (single-use) and secondary (rechargeable) batteries. Primary batteries offer convenience and longer shelf life, while secondary batteries provide the advantage of reusability but may require additional charging infrastructure.
-
Battery Metrics: Battery metrics play a vital role in evaluating battery performance. Important metrics include capacity (amount of charge the battery can store), voltage (electrical potential difference), energy density (amount of energy stored per unit volume or weight), and power density (rate at which energy can be delivered). Understanding these metrics helps in selecting batteries that meet specific power requirements.
-
Energy Density and Power Availability: Energy density refers to the amount of energy stored in a battery per unit volume or weight. Power availability relates to the battery’s ability to deliver energy at a specific rate. Balancing energy density and power availability is crucial for applications with varying power demands, as higher energy density may come at the cost of lower power availability.
-
Durability and Lifetime: Durability and lifetime considerations involve assessing the battery’s ability to withstand environmental conditions, temperature variations, and the number of charge-discharge cycles it can endure. Choosing batteries with suitable durability and longer lifetimes ensures reliable performance and reduces the need for frequent replacements.
-
Environmental Impact: Considering the environmental impact of batteries is increasingly important. Evaluating factors such as battery chemistry, recyclability, and disposal methods helps in selecting batteries that minimize environmental harm and align with sustainability goals.
Determining C-Rate for Performance Testing
-
C-Rate Definition: The C-rate is a charge or discharge current normalized to the battery’s capacity. It represents the rate at which the battery is charged or discharged relative to its maximum capacity. For example, a C-rate of 1C means that the battery can be charged or discharged in one hour, drawing a capacity equal to its nominal capacity.
-
Performance Testing: Performance testing involves evaluating how a battery performs under specific conditions. When determining the C-rate for performance testing, it is important to select an appropriate charge or discharge current that aligns with the testing requirements. The C-rate helps in standardizing the testing conditions and comparing the performance of different batteries.
-
Measuring Charge or Discharge Current: To determine the C-rate for performance testing, the charge or discharge current needs to be measured accurately. This can be done using specialized battery analyzers or testing equipment. By applying a constant current load or charge, the C-rate can be calculated based on the battery’s nominal capacity.
-
Evaluating Performance: Once the C-rate is determined, it can be used to assess the performance of the battery under specific testing conditions. Higher C-rates may result in higher discharge currents and shorter discharge times, indicating the battery’s ability to deliver power quickly. Lower C-rates may reflect longer discharge times and higher capacity, suitable for applications with lower power demands.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding battery C-rate is paramount for assessing and selecting batteries for various applications. By grasping the relationship between capacity, discharge rate, and C-rate, engineers and practitioners can make informed decisions that optimize battery performance and enhance system reliability.
FAQs
What info is required for C Rating Calculator?
- To use a C-rating calculator, you need the battery’s capacity (in Ah) and the maximum current draw (in A).
- The C-rating calculator calculates the time of charge or discharge based on these inputs.
- It helps determine the battery’s ability to deliver or receive current efficiently.
What’s the formula for charge/discharge time from C Rating?
- To calculate the discharge time from the C Rating, divide the battery’s capacity (in Ah) by the C Rating.
- This will give you the time in hours that the battery can deliver a specific current.
- For the charge time, divide the battery’s capacity (in Ah) by the C Rating to determine the time in hours required for a complete charge.
How does C Rating influence charge/discharge time?
- The C Rating determines the charge/discharge time of a battery.
- A higher C Rating means faster charging or discharging, resulting in shorter charge/discharge times.
- For example, a battery with a 1C rating can be fully charged or discharged in approximately 60 minutes, while a battery with a 2C rating can achieve the same in just 30 minutes.
- The C Rating directly affects the battery’s ability to deliver or receive energy efficiently.
Why Manufacturers Adjust Capacity at Different C Rates
-
Discrepancies at Different C Rates: When a battery is discharged at different C rates, the capacity readings can differ. This is because the C rate affects how quickly the battery discharges, and faster rates can result in lower apparent capacity.
-
Capacity Offsets: To account for these discrepancies, manufacturers provide what are known as capacity offsets. These are adjustments made to the stated capacity of the battery to more accurately reflect its performance at different discharge rates.
-
Importance: These adjustments are important for providing accurate information about the battery’s performance under different conditions. This can help users choose the right battery for their needs and ensure their device operates effectively.
How to Calculate Output from Battery C Rating
-
Understanding C Ratings: The C rating of a battery tells us how quickly it can be charged or discharged. For example, a 1C rating means the battery can be fully charged or discharged in one hour, a 2C rating in half an hour, and a 0.5C rating in two hours.
-
The Formula: The formula to calculate the charge or discharge time from the C rating is t = 1/Cr for hours or time = 60mins / Cr for minutes. This means that if you know the C rating of your battery, you can easily calculate how long it will take to charge or discharge.
-
Practical Applications: This calculation can be useful in many situations. For example, if you’re using a battery to power a device and you know how long you need the device to run, you can use this calculation to choose a battery with the right C rating.
What C Rating Means for Charge/Discharge Rates
-
C Rating: The C rating of a battery is a measure of the current at which the battery is charged and discharged. It’s like a speed limit for the battery, controlling how fast it can charge and discharge.
-
1C Rate: Batteries are typically rated and labelled at the 1C rate. This means that a fully charged battery with a capacity of 10Ah (ampere-hours) should be able to discharge at a rate of 10 amps for one hour.
-
Importance: Understanding the C rating is crucial for ensuring the longevity of your battery and the optimal operation of your device. Using a battery at a higher C rate than it’s rated for can lead to decreased battery life and potential damage to your device.
How C Rates Dictate Battery Service Times
-
The Formula: To calculate the service time of a battery, divide the battery’s capacity (in mAh) by 1000 to get its capacity in Ah. Then, multiply the C rating by this number to get the available amps. Finally, divide 60 by the C rating to get the service time in minutes.
-
An Example: For instance, a 2300mAh battery has a capacity of 2.3Ah. If its C rating is 30C, it has 69 Amps available. Its service time would be 2 minutes.
-
Practical Implications: Understanding this calculation can help you estimate how long a battery will last under different conditions. This can be especially useful when choosing a battery for a specific device or application.
How to Discover a Battery’s C Rating
-
Importance of C Rating: The C rating of a battery is a measure of how quickly it can be charged or discharged. Operating a battery beyond its recommended C rating can lead to overheating, reduced lifespan, and even safety hazards.
-
Choosing the Right Battery: When choosing a battery, it’s important to select one with an appropriate C rating for your device. This will ensure that the battery can handle the power demands of your device without overheating or failing prematurely.
-
Safety Considerations: Always remember that using a battery with a higher C rating than your device requires can lead to safety hazards. Always choose a battery with a C rating that matches or slightly exceeds the power demands of your device.
Can you provide an example of a 100Ah lithium battery C rate?
-
Definition of C Rate: The C rate of a battery refers to its charge and discharge rate. It is a measure of the battery’s capacity and determines how quickly it can deliver or store energy. The C rate is typically expressed as a multiple of the battery’s nominal capacity.
-
Example of a 100Ah Lithium Battery C Rate: Let’s consider a 100Ah lithium battery with a C10 rating. This means that the battery can discharge at a rate of 10A (10 amps) for 10 hours until it is fully discharged. In other words, it can deliver a continuous current of 10A for 10 hours.
-
Significance of C Rate: The C rate is important because it determines the battery’s capacity to meet specific power requirements. A higher C rate indicates that the battery can deliver energy more quickly, making it suitable for applications with higher power demands. Understanding the C rate allows users to select the appropriate battery for their specific needs.