36V battery for golf cart, choose lead acid battery or lithium batteries?
Are you looking to power up your golf cart with a reliable 36V battery but unsure whether to go for traditional lead acid or cutting-edge lithium technology? Let’s dive into the world of golf cart batteries and explore the pros and cons of each option to help you make an informed decision. Whether you’re a casual weekend golfer or a dedicated enthusiast, choosing the right battery is crucial for maximizing performance on the green.
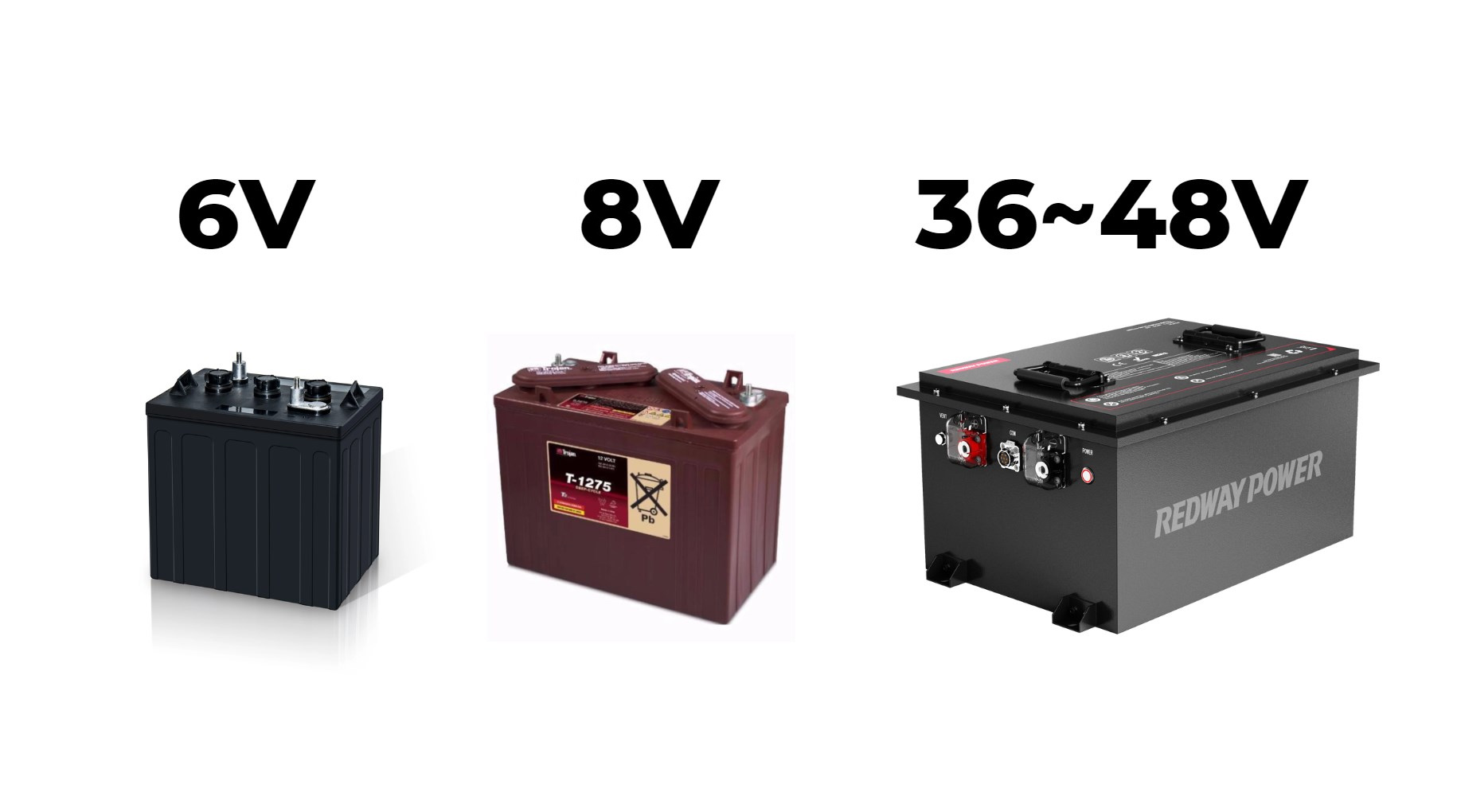
Pros and cons of lead acid batteries
Lead acid batteries have been a traditional choice for powering golf carts. One of the advantages of lead acid batteries is their affordability compared to lithium alternatives. They are widely available and have a proven track record in the industry.
However, lead acid batteries tend to be heavier and bulkier than lithium options, which can affect the overall performance of your golf cart. Additionally, they require more frequent maintenance such as topping up electrolyte levels and cleaning terminals.
Another downside is that lead acid batteries have a shorter lifespan compared to lithium batteries. This means you may need to replace them more often, adding to long-term costs.
On the positive side, lead acid batteries are generally more forgiving when it comes to charging practices and can handle overcharging better than lithium counterparts. Weighing these pros and cons will help you decide if lead acid batteries are the right choice for your golf cart needs.
Pros and cons of lithium batteries
Lithium batteries are known for their lightweight and compact design, making them a popular choice for golf cart owners looking to maximize space and efficiency. The high energy density of lithium batteries allows for longer driving ranges on a single charge, perfect for those long days out on the course.
One of the main advantages of lithium batteries is their fast charging capabilities. With shorter charging times compared to lead acid batteries, you can spend less time waiting around and more time enjoying your game. Additionally, lithium batteries have a longer lifespan and can withstand more charge-discharge cycles than lead acid alternatives.
However, it’s important to note that lithium batteries come with a higher price tag upfront. While they may save you money in the long run due to their longevity and performance benefits, the initial investment can be a deterrent for some golf cart owners. Moreover, proper handling and maintenance are crucial to ensure safety when using lithium batteries in your golf cart.
Comparison of battery life and maintenance
When it comes to comparing the battery life and maintenance of lead acid batteries versus lithium batteries for your golf cart, there are some key differences to consider.
Lead acid batteries are known for being more affordable upfront, but they typically have a shorter lifespan compared to lithium batteries. On the other hand, lithium batteries tend to last longer and require less maintenance over time.
In terms of maintenance, lead acid batteries may need regular topping up with distilled water and cleaning of terminals to prevent corrosion. Lithium batteries generally require minimal upkeep aside from ensuring proper charging practices.
When deciding between the two types of batteries, it’s essential to weigh factors such as how frequently you use your golf cart, budget constraints, and whether you prioritize longevity or initial cost savings.
Understanding the nuances in battery life and maintenance can help you make an informed decision that aligns with your specific needs and preferences.
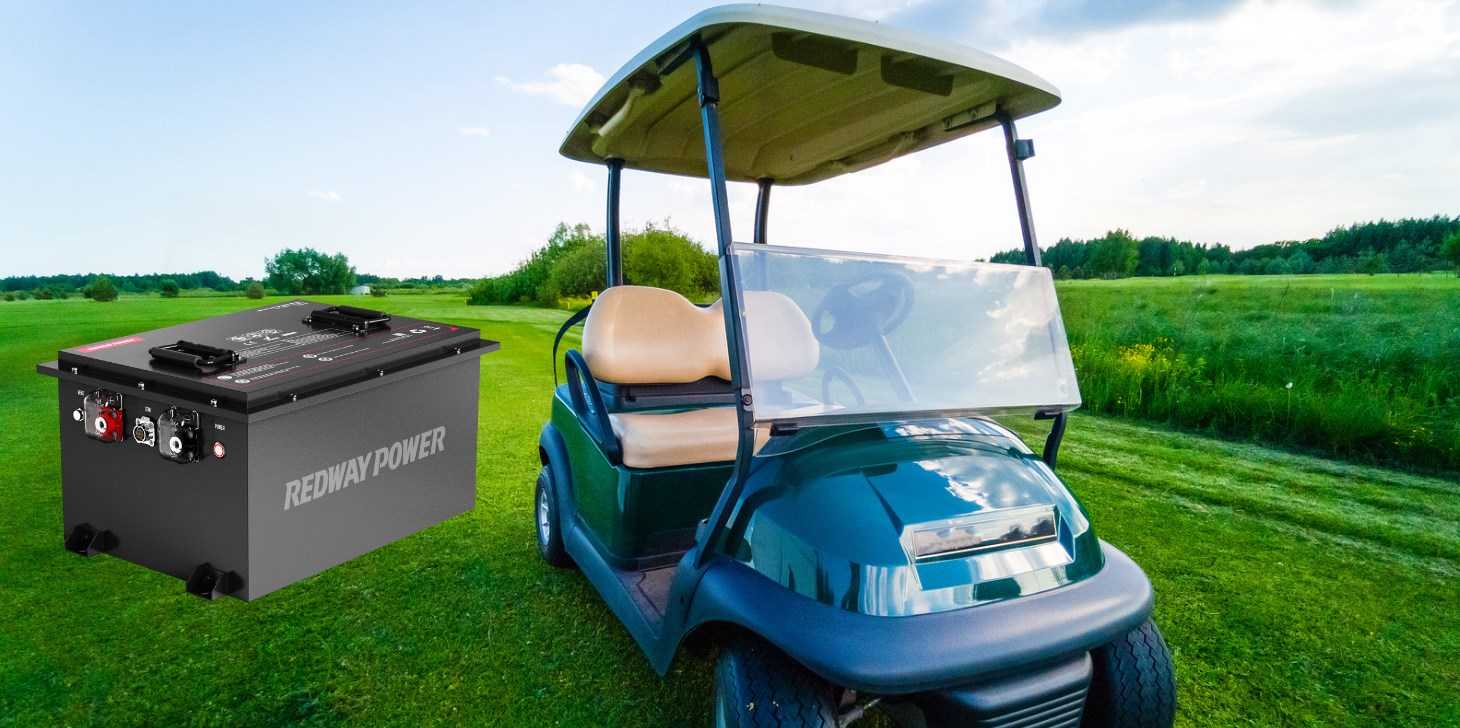
Factors to consider before choosing a 36V battery for your golf cart
When considering a 36V battery for your golf cart, there are several factors to keep in mind. Think about the size and weight of the battery. Will it fit within the designated space on your cart without compromising performance? Additionally, consider the voltage requirements of your specific golf cart model to ensure compatibility.
Another important factor is the lifespan of the battery. How long do you expect it to last before needing replacement? Look into the manufacturer‘s warranty and customer reviews to gauge its durability. Moreover, think about how often you plan to use your golf cart and if a longer-lasting battery would be more cost-effective in the long run.
Maintenance is also crucial – do you prefer a low-maintenance lead acid battery or a higher maintenance lithium option with potentially longer life expectancy? Factor in your budget and weigh the initial cost against potential savings over time based on efficiency and longevity.
Cost comparison between lead acid and lithium batteries
When it comes to choosing a 36V battery for your golf cart, one important factor to consider is the cost. Lead acid batteries are generally more affordable upfront compared to lithium batteries. This can be appealing if you’re on a tight budget or looking for a quick fix.
On the other hand, while lithium batteries may have a higher initial cost, they often prove to be more cost-effective in the long run due to their longer lifespan and lower maintenance requirements. With lead acid batteries, you might end up spending more on replacements and upkeep over time.
It’s essential to weigh the upfront costs against the potential savings down the line when deciding between these two types of batteries. Consider your budget, how often you use your golf cart, and how long you plan on keeping it before making a decision based on cost alone.
Tips for maximizing the lifespan of your chosen battery
Looking to get the most out of your golf cart battery? Here are some tips to help you maximize its lifespan.
Make sure to regularly check the water levels in your lead acid battery and top them up as needed. Proper maintenance can extend the life of your battery significantly.
Avoid overcharging or undercharging your lithium battery. Follow manufacturer guidelines for charging cycles to prevent damage and prolong its lifespan.
Keep your batteries clean and free from corrosion. Regularly inspect terminals and cables for any signs of wear or build-up that could affect performance.
Store your batteries properly during periods of non-use. Extreme temperatures can impact battery performance, so ensure they are stored in a cool, dry place when not in use.
Consider investing in a quality charger designed specifically for your type of battery. This can help maintain optimal performance and extend the overall lifespan of your chosen 36V golf cart battery.
Conclusion
When it comes to choosing the right 36V battery for your golf cart, there are several factors to consider. Lead acid batteries offer affordability and a proven track record but require more maintenance. On the other hand, lithium batteries provide longer lifespan and better performance but come with a higher price tag.
The decision between lead acid and lithium batteries will depend on your budget, usage frequency, and preference for maintenance requirements. Whichever option you choose, proper care and maintenance will help maximize the lifespan of your golf cart battery.
Consider all the pros and cons discussed in this article before making your decision. Whether you opt for lead acid or lithium batteries, ensuring that your battery is well-maintained will ensure optimal performance on the golf course. Choose wisely to enjoy many rounds of smooth rides with your golf cart!