Batteries are present in almost all aspects of our lives. From the small button cells that power our watches to the huge batteries that power electric cars, they form an essential part of our daily lives. But have you ever wondered how batteries work, or how they store energy? The answer lies in understanding the flow of electrons in a battery.
Let’s Talk about the Electron Flow
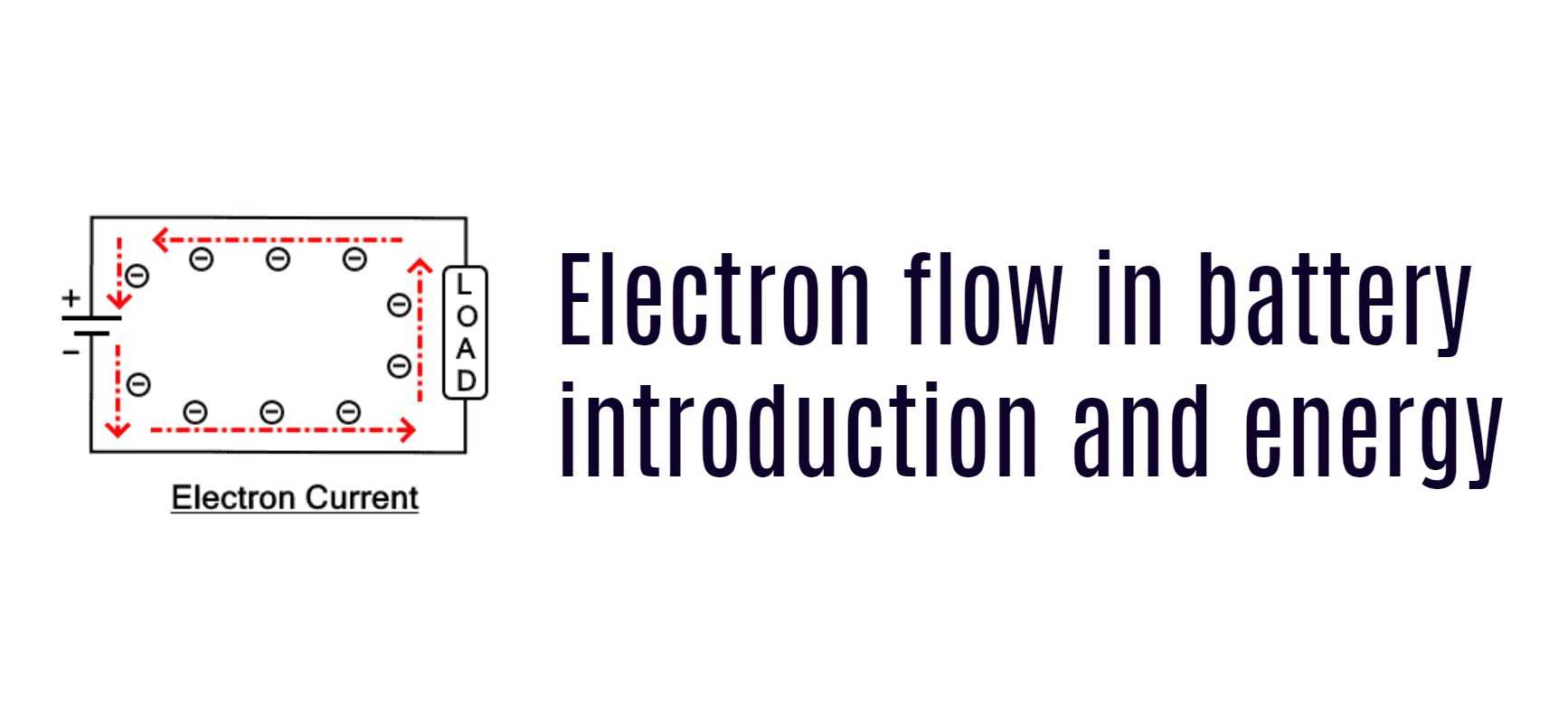
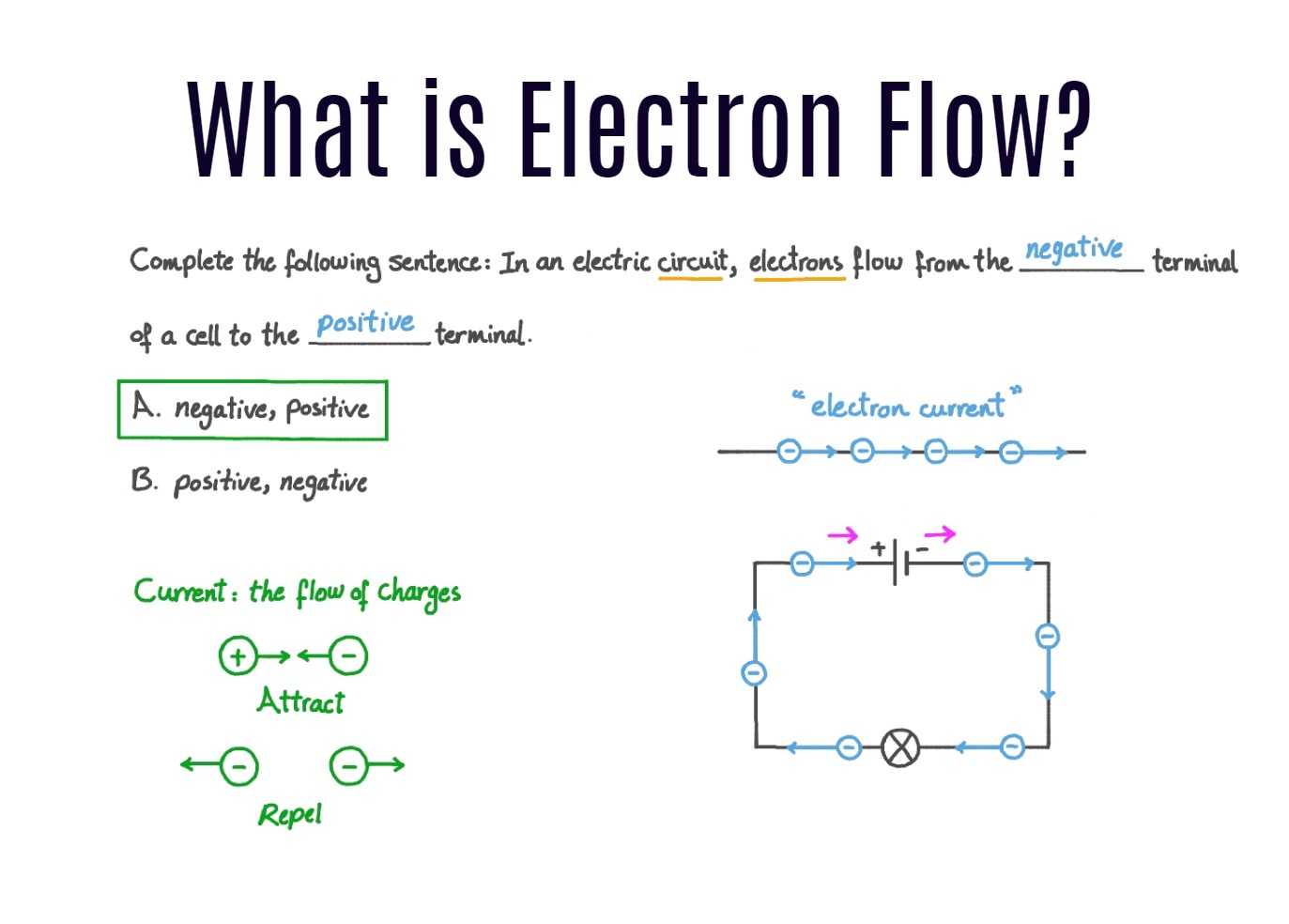
Electrons are the tiny subatomic particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom. When these electrons flow from one atom to another, they create an electrical current. Batteries use this flow of electrons to power devices. In simple terms, a battery works by moving electrons from one electrode to another, creating a flow of current.
The flow of electrons in a battery is controlled by a chemical reaction that occurs between the electrodes and the electrolyte. The electrolyte is a solution that contains ions, which are charged particles that carry the electrical charge. When the battery is charged, the chemical reaction forces electrons from the positive electrode to the negative electrode, where they are stored. When the battery is discharged, the electrons flow back from the negative electrode to the positive electrode, creating an electrical current.
Understanding the Anatomy of a Battery
A battery is made up of two electrodes, a positive electrode and a negative electrode, and an electrolyte. The positive electrode is typically made of a metal oxide, while the negative electrode is usually made of a metal. The electrolyte is a solution that contains ions, which carry the electrical charge.
When a battery is connected to a circuit, the chemical reaction between the electrodes and the electrolyte causes the flow of electrons from the negative electrode to the positive electrode. The flow of electrons generates a current that powers the device.
How do Batteries Store Energy?
Batteries store energy by converting chemical energy into electrical energy. When a battery is charged, the chemical reaction between the electrodes and the electrolyte stores energy in the form of electrons in the negative electrode. When the battery is discharged, the stored electrons flow back to the positive electrode, creating an electrical current that can power a device.
The amount of energy that a battery can store depends on its capacity. Battery capacity is measured in ampere-hours (Ah) and represents the amount of charge that a battery can deliver over a period of time. The higher the capacity, the more energy a battery can store.
The Science behind a Battery’s Energy
The energy stored in a battery is a result of the chemical reaction that occurs between the electrodes and the electrolyte. This reaction generates a voltage, which is the electrical potential difference between the positive and negative electrodes.
The voltage of a battery determines its energy capacity, which is the amount of energy that the battery can deliver over a period of time. The higher the voltage, the more energy a battery can store.
A World without Batteries – Can You Imagine?
Batteries have become an integral part of our lives. From powering our phones and laptops to running electric vehicles and storing solar energy, they have revolutionized the way we live. But can you imagine a world without batteries?
Without batteries, we would not have portable devices, electric cars, or renewable energy storage. Life would be very different without the spark that powers our lives. So the next time you use a battery-powered device, take a moment to appreciate the science and technology that makes it possible.
Batteries may seem like a small and unassuming component of our lives, but they play an essential role in powering our world. Understanding how they work and store energy can help us appreciate the science and technology behind them. So the next time you use a battery, remember the electrons flowing inside it and the energy it holds.
FAQs
What is electron flow in battery?
- Electron Flow in Batteries: Electron flow in a battery refers to the movement of electrons from one electrode to another, creating an electrical current. This flow is controlled by chemical reactions between the electrodes and the electrolyte.
- Role of Chemical Reactions: Batteries utilize chemical reactions to force electrons from the positive electrode to the negative electrode during charging. These electrons are stored until the battery is discharged, and they flow back from the negative electrode to the positive electrode, generating an electrical current.
- Understanding Battery Function: Understanding electron flow in batteries is crucial to comprehend how batteries work and power various devices. It provides insights into the fundamental principles behind battery operation and the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy.
What is the electron flow of a battery terminal?
- Electron Flow in Battery Terminals: Electrons flow from the negative terminal to the positive terminal within a battery. This flow is due to the negative charge of electrons and their attraction to the positive terminal.
- Generation of Electric Current: The movement of electrons within the battery creates an electric current. This current can be used to power devices and perform various electrical functions.
- Conventional Current Flow: It is important to note that conventional current flow is considered to be in the opposite direction, from the positive terminal to the negative terminal. However, when discussing electron flow, we focus on the actual movement of electrons within the battery.
What is the basic principle of battery?
- Basic Principle of a Battery: A battery operates by converting chemical energy into electrical energy through the oxidation and reduction reactions of an electrolyte with metals. It consists of two dissimilar metals (electrodes) and an electrolyte that enables the flow of electrons.
- Electrodes and Electrolyte: The battery utilizes two different metals as electrodes and an electrolyte to create a potential difference. The cathode, which is the negative terminal, and the anode, which is the positive terminal, play crucial roles in the battery’s functioning.
- Electron Affinity: The electron affinity of the metals determines which metal gains or loses electrons, influencing the direction of the current flow. This phenomenon is essential in understanding the behavior of electrons within the battery and the overall operation of the device.
Why electrons flow in a wire when connected to a battery?
- Electron Flow in a Wire: When a wire is connected to a battery, electrons flow from the negative terminal to the positive terminal. This flow is driven by the electric field created by the battery, which exerts a force on the electrons.
- Electric Current: The movement of electrons in a wire constitutes electric current. It is the flow of electric charge through a conductor, driven by the presence of an electric field.
- Role of a Resistor: The presence of a resistor in the circuit regulates the flow of electrons and controls the current. It slows down the movement of electrons, limiting the amount of current flowing through the wire.
How does current flow through a battery?
- Current Flow in a Battery: When a battery is connected in a circuit, current flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal. This flow of current is due to the movement of electrons.
- Movement of Electrons: Inside the battery, chemical reactions occur that create a potential difference between the terminals. The positive terminal becomes positively charged, attracting electrons from the negative terminal.
- External Circuit: These electrons then flow through the external circuit, powering devices or performing work. The flow of current is essential for the functioning of electrical circuits and the utilization of electrical energy stored in the battery.
How does energy flow in a battery?
- Electron Movement: Energy flows in a battery through the movement of electrons. Chemical reactions occur between the electrodes and the electrolyte, creating a flow of electrons in a circuit.
- Role of Electrodes and Electrolyte: The positive electrode (cathode) attracts electrons, while the negative electrode (anode) releases electrons. The electrolyte facilitates the movement of electrons and controls the flow of energy.
- Conversion of Chemical Energy: The energy is stored in the chemical reactions that occur inside the battery. When the battery is in use, the stored energy is converted into electrical energy, which can power devices or perform work.