Battery size charts list dimensions (length, width, height) in inches/cm. They use group numbers (like 24, 27, 31) to represent standard sizes. Match your vehicle’s or device’s needs to the dimensions listed in the chart to find the right battery!
What is BCI Battery?
BCI stands for Battery Council International, an organization that establishes standards for battery specifications, including group sizes. BCI provides guidelines that help manufacturers create batteries compatible with various vehicles, ensuring proper fitment and performance across different applications.
Understanding the Battery Group Size Chart
A battery group size chart is a reference tool that lists various battery sizes along with their dimensions and specifications. It helps consumers identify compatible batteries for their vehicles, ensuring the correct fit for optimal performance.
Automotive battery group sizes are industry standards that define a battery’s physical dimensions (length, width, height), terminal placement, and sometimes chemistry. Charts categorize batteries by group size, ensuring proper fit in vehicles. Check your car’s owner manual or use online fitment guides to identify the correct group size for replacement.
Need the right car battery? A size chart tells you what fits! It shows battery group sizes, dimensions, and where the posts go. Also, check the CCA for cold starts. Use the chart to match your car’s needs, so everything works perfectly.
Using the right group size prevents issues related to improper fit and insufficient power supply.
- Meaning of Battery Group Size Chart: The chart standardizes batteries based on size and terminal placement, indicating length, width, height, and polarity. Each number signifies a different set of dimensions, with larger numbers denoting larger batteries.
- Choosing the Right Size: Smaller vehicles like compacts need smaller group sizes for a snug fit, avoiding issues from too-large or too-small batteries. Your owner’s manual or online resources from reliable sources can help identify the right size for your vehicle.
- Impact of Incorrect Sizes: Incorrect sizes can lead to problems. Small batteries might not power your car enough, while large ones could damage wiring or components. Trucks and SUVs typically need larger batteries due to their greater electrical demands.
- Conclusion: Understanding the chart ensures you select the right battery size, avoiding performance issues and extending the battery’s lifespan. Always match the right size to your vehicle type for optimal performance.
| BCI Group Number |
Maximum Overall Dimensions | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Millimeters | Inches | Redway Battery Models | |||||
| L | W | H | L | W | H | ||
| Passenger Car and Light Commercial Batteries 12-Volt (6 Cells) | |||||||
| 21 | 208 | 173 | 222 | 8 3/16 | 6 13/16 | 8 3/4 | * |
| 22F | 241 | 175 | 211 | 9 1/2 | 6 7/8 | 8 5/16 | * |
| 22HF | 241 | 175 | 229 | 9 1/2 | 6 7/8 | 9 | * |
| 22NF | 240 | 140 | 227 | 9 7/16 | 5 1/2 | 8 15/16 | * |
| 22R | 229 | 175 | 211 | 9 | 6 7/8 | 8 5/16 | * |
| 24 | 260 | 173 | 225 | 10 1/4 | 6 13/16 | 8 7/8 | 12V75Ah 12V90Ah 12V105Ah 12V100Ah 24V50Ah |
| 24F | 273 | 173 | 229 | 10 3/4 | 6 13/16 | 9 | * |
| 24H | 260 | 173 | 238 | 10 1/4 | 6 13/16 | 9 3/8 | * |
| 24R | 260 | 173 | 229 | 10 1/4 | 6 13/16 | 9 | * |
| 24T | 260 | 173 | 248 | 10 1/4 | 6 13/16 | 9 3/4 | * |
| 25 | 230 | 175 | 225 | 9 1/16 | 6 7/8 | 8 7/8 | * |
| 26 | 208 | 173 | 197 | 8 3/16 | 6 13/16 | 7 3/4 | * |
| 26R | 208 | 173 | 197 | 8 3/16 | 6 13/16 | 7 3/4 | * |
| 27 | 306 | 173 | 225 | 12 1/16 | 6 13/16 | 8 7/8 | 12V90Ah 12V105Ah |
| 27F | 318 | 173 | 227 | 12 1/2 | 6 13/16 | 8 15/16 | * |
| 27H | 298 | 173 | 235 | 11 3/4 | 6 13/16 | 9 1/4 | * |
| 29NF | 330 | 140 | 227 | 13 | 5 1/2 | 8 15/16 | * |
| 33 | 338 | 173 | 238 | 13 5/16 | 6 13/16 | 9 3/8 | * |
| 34 | 260 | 173 | 200 | 10 1/4 | 6 13/16 | 7 7/8 | 12V75Ah-ST |
| 34R | 260 | 173 | 200 | 10 1/4 | 6 13/16 | 7 7/8 | * |
| 35 | 230 | 175 | 225 | 9 1/16 | 6 7/8 | 8 7/8 | * |
| 36R | 263 | 183 | 206 | 10 3/8 | 7 1/4 | 8 1/8 | * |
| 40R | 277 | 175 | 175 | 10 15/16 | 6 7/8 | 6 7/8 | * |
| 41 | 293 | 175 | 175 | 11 3/16 | 6 7/8 | 6 7/8 | * |
| 42 | 243 | 173 | 173 | 9 5/16 | 6 13/16 | 6 13/16 | * |
| 43 | 334 | 175 | 205 | 13 1/8 | 6 7/8 | 8 1/16 | * |
| 45 | 240 | 140 | 227 | 9 7/16 | 5 1/2 | 8 15/16 | * |
| 46 | 273 | 173 | 229 | 10 3/4 | 6 13/16 | 9 | * |
| 47 | 246 | 175 | 190 | 9 11/16 | 6 7/8 | 7 1/2 | * |
| 48 | 306 | 175 | 192 | 12 1/16 | 6 7/8 | 7 9/16 | * |
| 49 | 381 | 175 | 192 | 15 | 6 7/8 | 7 3/16 | * |
| 50 | 343 | 127 | 254 | 13 1/2 | 5 | 10 | * |
| 51 | 238 | 129 | 223 | 9 3/8 | 5 1/16 | 8 13/16 | * |
| 51R | 238 | 129 | 223 | 9 3/8 | 5 1/16 | 8 13/16 | * |
| 52 | 186 | 147 | 210 | 7 5/16 | 5 13/16 | 8 1/4 | * |
| 53 | 330 | 119 | 210 | 13 | 4 11/16 | 8 1/4 | * |
| 54 | 186 | 154 | 212 | 7 5/16 | 6 1/16 | 8 3/8 | * |
| 55 | 218 | 154 | 212 | 8 5/8 | 6 1/16 | 8 3/8 | * |
| 56 | 254 | 154 | 212 | 10 | 6 1/16 | 8 3/8 | * |
| 57 | 205 | 183 | 177 | 8 1/16 | 7 3/16 | 6 15/16 | * |
| 58 | 255 | 183 | 177 | 10 1/16 | 7 3/16 | 6 15/16 | * |
| 58R | 255 | 183 | 177 | 10 1/16 | 7 3/16 | 6 15/16 | * |
| 59 | 255 | 193 | 196 | 10 1/16 | 7 5/8 | 7 3/4 | * |
| 60 | 332 | 160 | 225 | 13 1/16 | 6 5/16 | 8 7/8 | * |
| 61 | 192 | 162 | 225 | 7 9/16 | 6 3/8 | 8 7/8 | * |
| 62 | 225 | 162 | 225 | 8 7/8 | 6 3/8 | 8 7/8 | * |
| 63 | 258 | 162 | 225 | 10 3/16 | 6 3/8 | 8 7/8 | * |
| 64 | 296 | 162 | 225 | 11 11/16 | 6 3/8 | 8 7/8 | * |
| 65 | 306 | 190 | 192 | 12 1/16 | 7 1/2 | 7 9/16 | * |
| 70 | 208 | 179 | 196 | 8 3/16 | 7 1/16 | 7 11/16 | * |
| 71 | 208 | 179 | 216 | 8 3/16 | 7 1/16 | 8 1/2 | * |
| 72 | 230 | 179 | 210 | 9 1/16 | 7 1/16 | 8 1/4 | * |
| 73 | 230 | 179 | 216 | 9 1/16 | 7 1/16 | 8 1/2 | * |
| 74 | 260 | 184 | 222 | 10 1/4 | 7 1/4 | 8 3/4 | * |
| 75 | 230 | 179 | 196 | 9 1/16 | 7 1/16 | 7 11/16 | * |
| 76 | 334 | 179 | 216 | 13 1/8 | 7 1/16 | 8 1/2 | * |
| 78 | 260 | 179 | 196 | 10 1/4 | 7 1/16 | 7 11/16 | 12V75Ah-ST |
| 85 | 230 | 173 | 203 | 9 1/16 | 6 13/16 | 8 | * |
| 86 | 230 | 173 | 203 | 9 1/16 | 6 13/16 | 8 | * |
| 90 | 246 | 175 | 175 | 9 11/16 | 6 7/8 | 6 7/8 | * |
| 91 | 280 | 175 | 175 | 11 | 6 7/8 | 6 7/8 | * |
| 92 | 317 | 175 | 175 | 12 1/2 | 6 7/8 | 6 7/8 | * |
| 93 | 354 | 175 | 175 | 15 | 6 7/8 | 6 7/8 | * |
| 95R | 394 | 175 | 190 | 15 9/16 | 6 7/8 | 7 1/2 | * |
| 96R | 242 | 173 | 175 | 9 9/16 | 6 13/16 | 6 7/8 | * |
| 97R | 252 | 175 | 190 | 9 15/16 | 6 7/8 | 7 1/2 | * |
| 98R | 283 | 175 | 190 | 11 3/16 | 6 7/8 | 7 1/2 | * |
| Passenger Car and Light Commercial Batteries 6-Volt (3 Cells) | |||||||
| 1 | 232 | 181 | 238 | 9 1/8 | 7 1/8 | 9 3/8 | * |
| 2 | 264 | 181 | 238 | 10 3/8 | 7 1/8 | 9 3/8 | * |
| 2E | 492 | 105 | 232 | 19 7/16 | 4 1/8 | 9 1/8 | * |
| 2N | 254 | 141 | 227 | 10 | 5 9/16 | 8 15/16 | * |
| 17HF | 187 | 175 | 229 | 7 3/8 | 6 7/8 | 9 | * |
| Heavy-duty Commercial Batteries 12-Volt (6 Cells) | |||||||
| 4D | 527 | 222 | 250 | 20 3/4 | 8 3/4 | 9 7/8 | * |
| 6D | 527 | 254 | 260 | 20 3/4 | 10 | 10 1/4 | * |
| 8D | 527 | 283 | 250 | 20 3/4 | 11 1/8 | 9 7/8 | 12V300Ah 24V150Ah 24V200Ah 48V60Ah 48V100Ah |
| 28 | 261 | 173 | 240 | 10 5/16 | 6 13/16 | 9 7/16 | * |
| 29H | 334 | 171 | 232 | 13 1/8 | 6 3/4 | 9 1/8 10 | * |
| 30H | 343 | 173 | 235 | 13 1/2 | 6 13/16 | 9 1/4 10 | * |
| 31 | 330 | 173 | 240 | 13 | 6 13/18 | 9 7/16 | 12V105Ah 12V120Ah 12V150Ah 24V60Ah |
| Electric Vehicle Batteries 6-Volt (3 Cells) | |||||||
| GC2 | 264 | 183 | 270 | 10 3/8 | 7 3/16 | 10 5/8 | * |
| GC2H | 264 | 183 | 295 | 10 3/8 | 7 3/16 | 11 5/8 | * |
Data excerpted from the BCI Battery Replacement Data Book.
Note 1: The complete BCI listing includes several categories not included here: Heavy-Duty motor Coach and Bus batteries, and Special Tractor Batteries (6 and 12-volt). BCI provides configuration diagrams and performance ratings as well. Contact BCI, 401 N. Michigan ave, Chicago IL 60611-4267, (312) 644-6610 for more information.
Note 2: The maximum height includes the terminal posts. Width and length measurements are generally to the widest point, including protruding flanges, except for hold-down flanges at the bottom of the battery. See the diagrams in the BCI battery Replacement Data Book for full details.
Note 3: * Contact Redway for custom order details.
Importance of Choosing the Right Battery Group Size
Choosing the correct battery group size is crucial for optimal vehicle performance and safety. A properly sized battery ensures a secure fit, preventing vibrations that can damage the battery or electrical system. It also guarantees sufficient power to start the engine and operate electrical components, enhancing reliability and longevity.
- Impact of Wrong Size: Using the wrong battery group size leads to poor connections, reduced power, and struggles starting, especially in cold weather. It can cause vibrations that harm other car parts.
- Charging System Effects: Mismatched sizes affect the charging system and can lead to early failure of both the battery and alternator, impacting their ability to charge properly.
- System Compatibility: Each car model has specific power needs. Choosing the right group size ensures compatibility, optimizing performance and preventing potential damage to your car’s electrical system.
Selecting the right battery group size matters more than you’d expect. It affects your car’s performance and longevity, so investing time in research or seeking expert advice pays off in reliability and cost savings.
(Also Read: BCI Battery Group Size Chart Guide and BCI Group Battery Factory Wholesale)
Different Types of Car Batteries and Their Corresponding Group Sizes
Car batteries come in various types, including lead-acid, AGM (Absorbed Glass Mat), and lithium-ion, each with specific group sizes. Common group sizes include 24, 27, 35, and 51, among others. Each size corresponds to different physical dimensions and terminal configurations, tailored to fit various vehicle makes and models.
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Reliable and budget-friendly, these come in various group sizes like Group 24 or Group 31, tailored to fit your car’s dimensions and power needs.
- AGM Batteries: AGM batteries use a soaked mat instead of liquid electrolyte, offering top-notch performance and durability, ideal for vehicles with high electrical demands.
- Specialized Batteries like Lithium-Ion: Hybrid or electric cars might need lithium-ion batteries with higher energy density and longer lifespans, though they tend to be pricier.
Ensure your battery matches your vehicle’s needs by checking the manufacturer‘s recommendations or using a Battery Group Size Chart Guide. Selecting the right group size ensures peak battery performance and prevents potential damage to your car’s electrical system. Understanding the different types of car batteries and their corresponding group sizes is essential before making a purchase. It saves money in the long run and keeps your car running smoothly.
How to Determine Your Car’s Battery Group Size
To determine your car’s battery group size, check the owner’s manual for specifications or look for a label near the battery compartment. You can also inspect the current battery for its group size designation or use online tools that match your vehicle’s make and model to recommended battery sizes.
- Check the Owner’s Manual: Start by consulting your car’s manual; it often specifies the recommended battery group size for your exact make and model.
- Inspect the Existing Battery: Look at your current battery for a label or stamp with a series of numbers and letters like 24F or H6 – these indicate the specific group size.
- Seek Professional Help: If needed, ask a mechanic or visit an auto parts store. They have tools and knowledge to identify the right battery group size for your vehicle.
Choosing the right battery group size matters because using the wrong size can cause electrical issues and potential damage to your car’s charging system. Make sure you get it right for optimal vehicle performance and the longevity of your car’s electrical components.
How Is Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) Measured and Why Does It Matter?
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) measures a battery’s ability to start an engine in cold temperatures, specifically at 0°F (-18°C) for 30 seconds without dropping below a specified voltage (usually 7.2 volts for a 12V battery). Higher CCA ratings indicate better performance in low temperatures. Chart: Understanding Cold Cranking Amps
| Temperature | Minimum Voltage | Time Duration | Required CCA |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0°F (-18°C) | 7.2 volts | 30 seconds | Varies by vehicle |
When choosing a battery for your vehicle, knowing the correct BCI group size is essential. The BCI group size standardizes dimensions and terminal placements, ensuring compatibility. For example, an auto battery group size 34 is common in many cars, while a group 70 battery fits larger vehicles like trucks and SUVs.
For heavy-duty applications, truck battery sizes vary, with options like group 47 batteries for specific models. Dimensions matter—group 70 battery dimensions are larger than compact group 47 batteries, so checking fitment is crucial. Whether you need an auto battery group size 34 or a robust truck battery, selecting the right BCI group size ensures optimal performance.
For reliable power, consider Redway Battery, Deep Cycle LiFePO4 Batteries Manufacturer, offering long-lasting energy solutions. Always verify your vehicle’s requirements before purchasing to avoid compatibility issues with truck battery sizes or other applications.
What Are Common Battery Sizes and Their Corresponding CCA Ratings?
Common battery sizes include Group 24 (around 600 CCA), Group 27 (around 700 CCA), and Group 31 (up to 900 CCA). These ratings vary based on the vehicle type; larger vehicles generally require higher CCA ratings to ensure reliable starting under challenging conditions.
Common battery sizes come with varying CCA ratings depending on their intended use:
- Group 24: Typically has a CCA rating between 600-800 amps, suitable for most cars.
- Group 27: Generally rated around 700-900 amps, often used in larger vehicles.
- Group 31: Can exceed 900 amps, ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Chart: Common Batteries and Their CCA Ratings
| Group Size | Typical CCA Rating | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 24 | 600-800 | Cars, RVs |
| 27 | 700-900 | Boats, larger vehicles |
| 31 | >900 | Heavy-duty trucks |
How to Choose the Right Battery Based on CCA for Your Vehicle?
To choose the right battery based on CCA, refer to your vehicle’s owner manual for specific recommendations. Match the required CCA rating with your vehicle’s engine size and consider colder climates where higher ratings are necessary for reliable starting performance.
Can Low Temperatures Affect My Vehicle’s Starting Ability?
Yes, low temperatures can significantly impact your vehicle’s starting ability by reducing battery capacity and efficiency. Cold weather increases oil viscosity, making it harder for the engine to turn over, which is why a high CCA rating is crucial in colder climates.
How Do I Know If My Battery Needs Replacement Based on CCA?
If your battery’s CCA rating falls below your vehicle’s requirements or if it struggles to start in cold weather, it may need replacement. Regular testing of your battery’s performance can help identify when it’s time to invest in a new one.
Tips for Maintaining Your Car’s Battery
To maintain your car’s battery, keep it clean and free of corrosion by regularly checking terminals. Ensure secure connections and avoid overcharging. Store the vehicle in a climate-controlled environment when possible. Additionally, periodically test the battery’s voltage and replace it if it shows signs of weakness or age.
These simple tips can help you keep it in top shape.
- Regular Inspections: Check for corrosion, loose connections, and leaks regularly. Clean off dirt and debris from the terminals to ensure a good connection.
- Keep it Clean: Maintain optimal performance by cleaning the battery with a baking soda-water mix to remove buildup on terminals gently.
- Mind Electrical Use: Avoid draining the battery by minimizing use of electrical accessories when the engine is off, like leaving lights on or using power-heavy devices.
- Drive Regularly: Prevent decreased battery life by driving the car at least once a week for a reasonable distance to keep it charged.
- Temperature Protection: Extreme temperatures affect battery performance. Park in shaded areas in summer and use insulation blankets in winter.
- Charging System Check: Test the car’s charging system occasionally to catch any issues early and avoid problems with the battery.
- Learn Jump-Starting: Understand how to safely jump-start a dead battery; it’s a valuable skill for emergencies.
Maintaining your car’s battery involves more than fluid checks; caring for components like belts contributes to overall vehicle health and longevity.
A battery group size chart is a crucial reference that lists battery sizes by their physical dimensions and terminal placements, helping you select the correct battery for your vehicle. The auto battery group size chart standardizes battery length, width, height, and terminal location to ensure proper fit and performance. Using the right size prevents installation issues and electrical problems. The automotive battery group size chart also helps compare cold cranking amps (CCA) and reserve capacity for your car’s needs. For example, the car battery group size chart includes popular groups like 24, 27, 31, and 35, each with specific dimensions. Checking the battery group sizes chart before purchase guarantees compatibility and optimal power delivery. For advanced power solutions, Redway Battery, Deep Cycle LiFePO4 Batteries Manufacturer, offers lithium batteries that fit many group sizes, providing longer life and better performance than traditional lead-acid batteries. Always consult a reliable auto battery group size chart to match your vehicle’s requirements precisely.
About BCI Group Sizes
FAQs
What do the different battery groups mean?
-
Battery Groups: Battery groups refer to the different sizes of batteries used in various applications. In the context of car batteries, the term “group” is used to identify the size of the battery. These groups are assigned based on factors such as physical dimensions, voltage, and capacity.
-
Classification by Organizations: Various organizations, including BCI, JIS, and DIN, establish battery group classifications. These organizations determine the group sizes based on industry standards and requirements. For example, BCI (Battery Council International) assigns group sizes like Group 24, Group 27, and Group 31 for automotive applications.
-
Compatibility and Performance: Battery groups ensure compatibility and optimal performance in different applications. Each group has its own unique characteristics, such as size, voltage, and capacity. It is important to select the appropriate battery group for specific needs to ensure reliable power supply.
Is a group 27 battery better than a group 24?
A group 27 battery is larger than a group 24 battery and can provide more power. These batteries are interchangeable if size constraints are not an issue. The specific power and capacity may vary depending on the manufacturer and battery technology. Group 27 batteries are suitable for applications that require higher power output and capacity, such as larger vehicles or systems with higher energy demands.
What’s the difference between a group 47 and 48 battery?
-
Group 47 Battery: Group 47 batteries are generally smaller in size compared to group 48 batteries. The specific dimensions and specifications may vary depending on the manufacturer and battery technology. It is important to consider the vehicle’s requirements and consult the vehicle’s manual or a professional to determine the appropriate battery size for optimal fitment and performance.
-
Group 48 Battery: Group 48 batteries are typically larger in size compared to group 47 batteries. The specific dimensions and specifications may vary depending on the manufacturer and battery technology. It is important to consider the vehicle’s requirements and consult the vehicle’s manual or a professional to determine the appropriate battery size for optimal fitment and performance.
What is the difference between Group 51 and 35 battery?
The difference between Group 51 and Group 35 batteries lies in their size and capacity. Group 51 batteries are smaller and are typically used in compact cars and hybrids, while Group 35 batteries offer higher capacity and are suitable for compact cars and light trucks. It’s important to choose the right battery group size for your vehicle to ensure optimal performance and avoid any fitment or electrical issues.
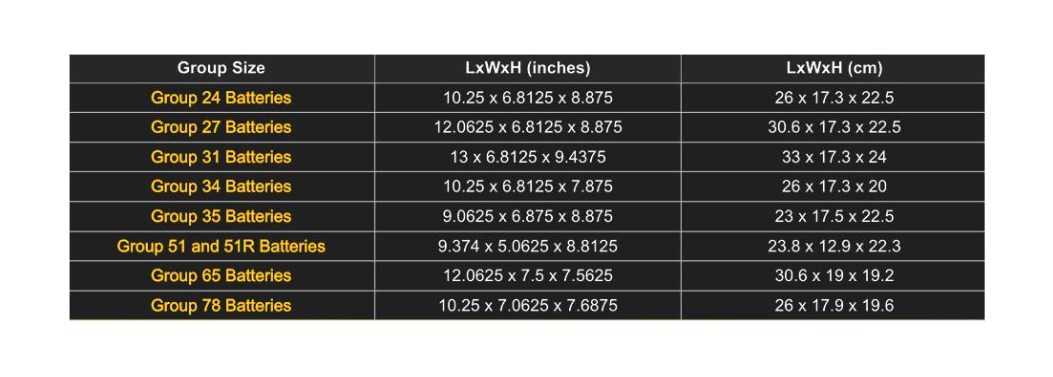
What are the battery group sizes? Battery group sizes refer to standardized classifications for automotive and marine batteries based on their physical dimensions and electrical specifications. These sizes help ensure compatibility with vehicles and equipment.
Is a group 27 battery bigger than a group 24? Generally, yes, a group 27 battery is larger than a group 24 battery in terms of both physical dimensions and capacity. Group sizes are numbered sequentially, with higher numbers typically indicating larger batteries.
Does battery group size really matter? Yes, battery group size matters as it determines whether a battery will fit in the designated battery compartment of a vehicle or equipment. Using the correct group size ensures proper fitment and electrical compatibility.
What does group size 75 mean on a battery? Group size 75 is a standardized classification for automotive batteries, indicating specific dimensions and electrical characteristics. It’s essential to match the group size with the vehicle’s requirements to ensure compatibility.
Are Group 34 and 78 batteries the same? No, Group 34 and Group 78 batteries are not the same. They differ in size, shape, and electrical specifications. Each group size is designed for specific applications and may not be interchangeable.
What happens if I use the wrong group size battery? Using the wrong group size battery can lead to improper fitment, electrical incompatibility, and potentially damage to the vehicle’s electrical system or equipment. It’s crucial to always use the recommended battery group size for your application.
Can I replace a group 24 battery with a group 27 battery? In some cases, it may be possible to replace a group 24 battery with a group 27 battery if the larger size fits within the designated battery compartment and the electrical specifications match the vehicle’s requirements. However, compatibility should be verified before installation.
What’s the difference between a Group 27 and a Group 31 marine battery? Group 27 and Group 31 marine batteries differ in size, capacity, and intended applications. Group 31 batteries are typically larger and have higher capacity compared to Group 27 batteries, making them suitable for larger marine vessels and applications with higher power demands.
How big is a group 31 battery? Group 31 batteries are larger than Group 27 batteries and have dimensions that vary depending on the manufacturer. Generally, they are approximately 13 inches in length, 6.75 inches in width, and 9.5 inches in height.
What vehicles use a group 27 battery? Group 27 batteries are commonly used in various vehicles, including boats, RVs, trucks, and some cars. They are suitable for applications requiring moderate to high electrical power.
What does a group 27 battery mean? Group 27 battery refers to a standardized classification for automotive and marine batteries, indicating specific dimensions and electrical characteristics. These batteries are commonly used in various vehicles and equipment.
How long will a group 27 deep cycle battery last? The lifespan of a group 27 deep cycle battery depends on various factors, including usage patterns, charging practices, maintenance, and environmental conditions. On average, a well-maintained deep cycle battery can last several years.

What is the most common battery group size? The most common battery group size may vary depending on the region and application. However, group sizes such as 24, 27, and 31 are among the more commonly used sizes for automotive and marine applications.
What does R mean on a battery? The “R” designation on a battery typically indicates a reverse terminal layout, where the positive and negative terminals are positioned differently compared to standard terminals. It’s essential to match the terminal layout with the vehicle’s requirements to ensure proper installation.
What is the difference between Group 27 and Group 31? Group 27 and Group 31 batteries differ in size, capacity, and intended applications. Group 31 batteries are larger and typically have higher capacity compared to Group 27 batteries, making them suitable for heavier-duty applications with higher power demands.







