Lithium-sulfur batteries are gaining attention for their potential to revolutionize energy storage. Offering longer lifespan and higher energy density compared to lithium-ion batteries, they hold promise for diverse applications. However, challenges such as limited cycle life and sulfur dissolution remain to be addressed for widespread adoption.
What is lithium-sulfur battery?
- Composition: Li-S batteries consist of lithium as the anode and sulfur as the cathode.
- High Specific Energy: These batteries offer a high specific energy, making them attractive for energy storage applications.
- Relatively Lightweight: Li-S batteries are relatively lightweight, providing a promising solution for portable and electric vehicle applications.
What are the basics of lithium-sulfur battery?
- Lithium Metal Anode: The battery includes a lithium metal anode for energy storage.
- Organic Liquid Electrolyte: An organic liquid electrolyte facilitates the movement of ions within the battery.
- Sulfur Composite Cathode: The cathode is composed of a sulfur composite material, enabling efficient energy conversion.
What is the lifespan of a lithium-sulfur battery?
- Lifespan: The estimated lifespan of a lithium-sulfur battery is approximately ten years.
- Sustainability Advantages: Lithium-sulfur batteries offer sustainability benefits over other lithium-ion batteries.
- Higher Capacity: These batteries have a higher capacity, allowing for greater energy storage.
What is the promise of a lithium-sulfur battery?
- Increased Energy Density: Li-S batteries have the potential to provide higher energy storage capacity compared to current lithium-ion batteries.
- Cost Reduction: These batteries offer the prospect of lower costs, making energy storage more affordable.
- Revolutionizing Energy Storage: Li-S batteries hold promise in revolutionizing the energy storage industry and enabling advancements in various applications.
Why are lithium-sulfur batteries better?
- Higher Energy Density: Li-S batteries offer a higher energy density per unit weight compared to other battery technologies.
- Efficient Energy Storage: The higher energy density of Li-S batteries enables more efficient energy storage solutions.
- Longer-Lasting Performance: With their higher energy density, Li-S batteries have the potential to provide longer-lasting energy storage capabilities.
What is the difference between lithium-ion battery and lithium-sulfur battery?
The difference between lithium-ion (Li-ion) and lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries lies in their electrochemical reactions, energy density, weight, and charging capabilities. Li-S batteries offer higher energy density and lighter weight, potentially enabling longer driving ranges and faster charging. Li-ion batteries are widely used but have lower energy density compared to Li-S batteries. Li-S batteries show promise for cleaner and more sustainable transportation.
- Higher Energy Density and Lighter Weight: Li-S batteries offer increased energy density and are lighter, allowing for greater energy storage and longer driving ranges.
- Faster Charging: Li-S batteries have the potential for faster charging, providing convenience and reducing charging times.
- Advancements for Sustainable Transportation: Li-S batteries show promise for cleaner and more sustainable transportation options, contributing to a greener future.
What is the range of lithium-sulfur battery?
- Extended Driving Range: Lithium-sulfur batteries offer the potential for a driving range of more than 400 miles.
- Higher Energy Capacity: With practical capacities of up to 500 watt-hours per kilogram at the pack level, Li-S batteries provide double the energy capacity of lithium-ion batteries.
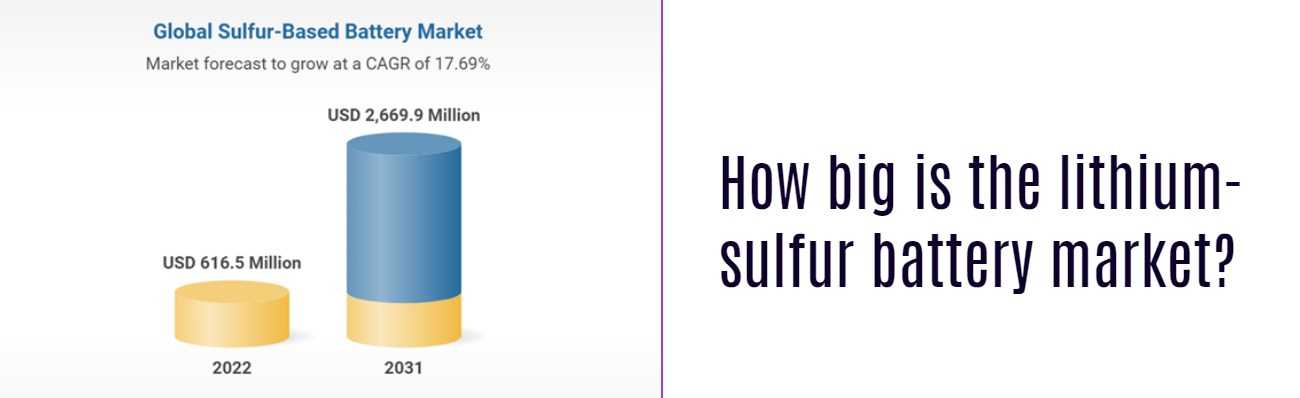
How big is the lithium-sulfur battery market?
- Market Size and Growth: The lithium-sulfur battery market is projected to reach USD 932.34 million by 2032, indicating significant growth opportunities.
- Demand in Various Industries: The increasing adoption of lithium-sulfur batteries in electric vehicles and energy storage systems drives market growth.
Is lithium-sulfur the future?
- Advantages of Li-S Batteries: Li-S batteries offer advantages such as low cost, high energy density, and long life.
- Future Potential: Li-S batteries have the potential to revolutionize the energy storage industry and contribute to the green energy transition.
What company is making lithium-sulfur batteries?
- Lyten’s Manufacturing Milestone: Lyten, based in Silicon Valley, has achieved success in producing lithium-sulfur batteries with a lithium metal anode.
- Scaling Next-Generation Batteries: Lyten’s success confirms the potential to scale the delivery of advanced lithium-sulfur batteries.
- Other Companies in the Field: NexTech Batteries Inc. and Zeta Energy are among the companies actively involved in advancing lithium-sulfur battery technology.
Is lithium-sulfur better than lithium-ion?
- Advantages of Li-S Batteries: Li-S batteries have the potential to be more environmentally friendly due to their utilization of abundant and cost-effective sulfur.
- Less Resource-Intensive: The extraction and processing of materials for Li-S batteries are less resource-intensive compared to Li-ion batteries that use materials like cobalt.
What is the problem with lithium-sulfur batteries?
- Polysulfide Dissolution: The dissolution of sulfur species (polysulfides) into the electrolyte was a significant problem in early Li-S batteries.
- Corrosion and Reduced Battery Life: The polysulfide shuttling effect caused corrosion and negatively impacted battery life and rechargeability.
- Stable Battery Performance: Maintaining stable performance in Li-S batteries required addressing the challenges caused by polysulfide dissolution.