Prominent manufacturers of Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries include BYD, CATL, LG Chem, and CALB, known for their innovation and reliability. LFP batteries offer enhanced safety, durability, and rapid charging capabilities, making them ideal for electric vehicles and renewable energy storage. Manufacturing involves cathode and anode preparation, assembly, and sealing processes. Continuous advancements in LFP technology promise a bright future for energy storage solutions.
What is Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) Battery?
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries have become a focal point in rechargeable battery technology. Belonging to the lithium-ion family, they stand out due to their unique composition and exceptional characteristics. Let’s explore what makes LFP batteries special:

- Cathode Composition:
- The core of an LFP battery features a cathode composed of lithium iron phosphate.
- This compound provides outstanding thermal stability, reducing the risk of overheating and ensuring safety—a critical advantage.
- Energy Density and Cycle Life:
- LFP batteries exhibit impressive energy density and boast a long cycle life.
- They can store more energy while maintaining performance over numerous charge-discharge cycles, offering durability and efficiency.
- Low Self-Discharge and High Discharge Rates:
- LFP batteries have a slower self-discharge rate, making them suitable for applications requiring extended storage.
- Their ability to handle high discharge rates without compromising performance makes them ideal for electric vehicles, meeting demands for quick bursts of power.
Lithium Iron Phosphate batteries combine enhanced safety, excellent energy density, extended cycle life, low self-discharge rates, and high-power capabilities. This unique blend has driven their popularity across various industries seeking reliable and sustainable energy solutions. Join us as we delve deeper into the world of LFP batteries!
Benefits of LFP Batteries
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries stand out for their diverse advantages, making them a preferred choice across various applications. Let’s explore the key benefits that set them apart:
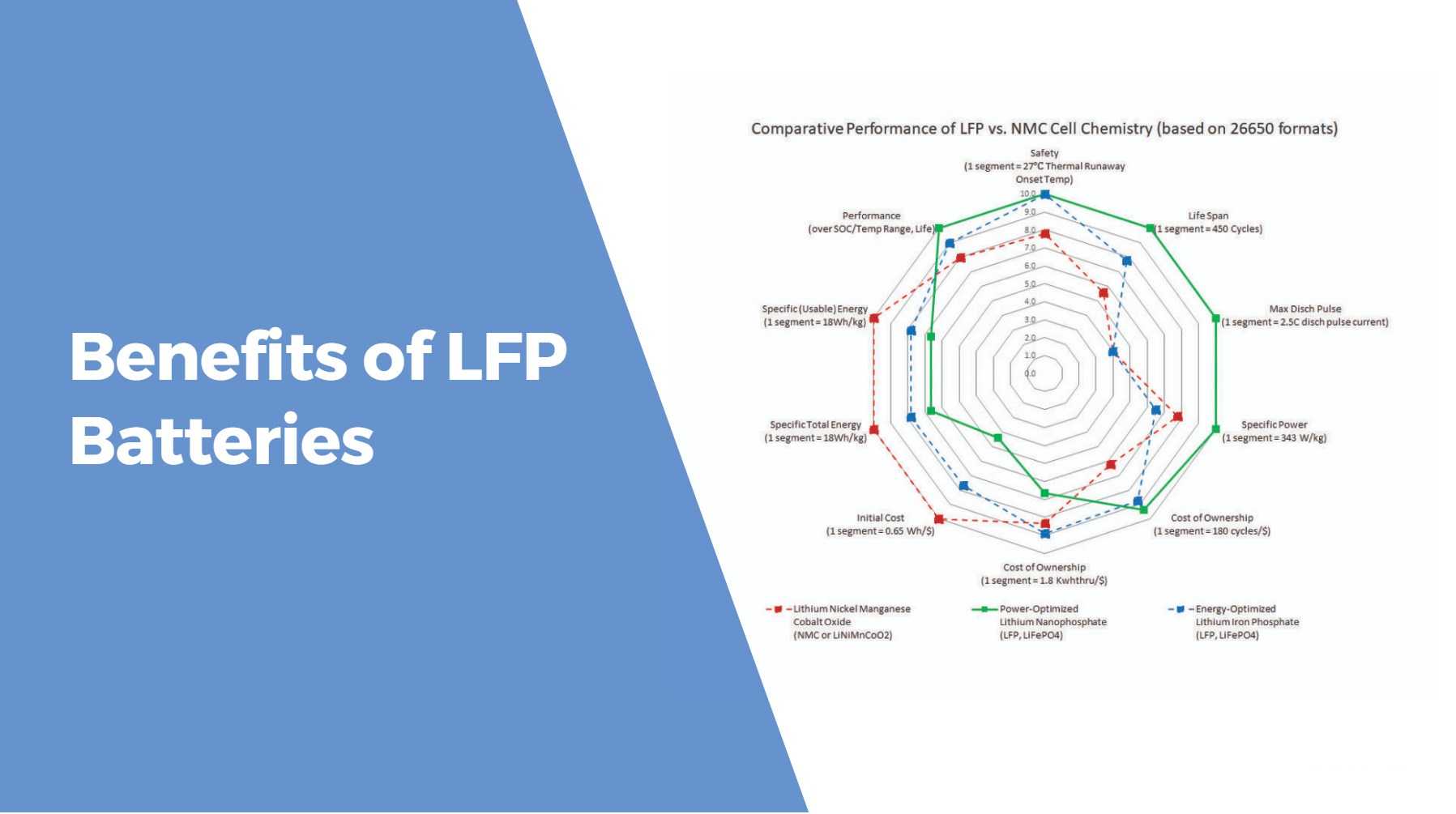
- Enhanced Safety:
- LFP batteries offer superior safety compared to other lithium-ion types.
- Their stability and reduced risk of overheating or fires provide users with a secure and reliable power solution.
- Long Lifespan and Durability:
- LFP batteries surpass traditional lead-acid batteries in lifespan.
- With the ability to endure thousands of charge cycles, they prove highly durable and cost-effective in the long term.
- Rapid Charging Capabilities:
- LFP batteries excel in rapid charging, accepting high charge currents.
- This feature is particularly valuable in industries where minimizing downtime is crucial.
- Performance in Extreme Temperatures:
- LFP batteries maintain consistent power output in extreme temperatures.
- Whether in scorching heat or freezing cold, they ensure reliable operation in harsh environmental conditions.
- High Energy Density:
- LFP technology offers higher energy density compared to cobalt-based lithium-ion chemistries.
- This results in compact and lightweight batteries that still deliver ample power, making them versatile for various applications.
The array of benefits provided by Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries positions them as an ideal choice for electric vehicles, renewable energy storage systems, and portable electronics.
Companies That Manufacture LFP Batteries
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries are manufactured by several reputable companies, each contributing to the innovation and growth of energy storage solutions. Let’s highlight some key players in the industry:

- BYD:
- Based in China, BYD is a leading global manufacturer of LFP batteries.
- Renowned for sustainability, BYD’s LFP batteries find applications in electric vehicles, renewable energy, and grid storage.
- CATL (Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Limited):
- CATL, another prominent Chinese company, is recognized for high-quality LFP batteries used in EVs and energy storage.
- Focused on research and development, CATL continually enhances its battery technology to meet consumer demands.
- LG Chem:
- LG Chem, hailing from South Korea, is an international player producing advanced lithium-ion batteries, including LFP variants.
- With a reputation for reliability, LG Chem supplies batteries to major automakers globally.
- CALB (China Aviation Lithium Battery Co., Ltd.):
- CALB is a significant LFP battery manufacturer, based in China.
- Specializing in customized solutions, CALB not only manufactures but also designs batteries tailored to specific customer needs.
These industry leaders invest heavily in research, development, and quality control, driving innovation and sustainable energy solutions. As the demand for clean energy grows, these companies play a crucial role in shaping the future of energy storage and electrification efforts across various sectors.
Comparison with Other Battery Types
In the realm of battery technology, lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries compete with various alternatives like lithium-ion (Li-ion), lead-acid, and nickel-based chemistries. Let’s explore the key differences:
- LFP vs. Li-ion Batteries:
- Safety: LFP batteries excel in safety, being more stable and less prone to overheating compared to Li-ion, which can experience thermal runaway.
- Energy Density: Li-ion batteries generally offer higher energy density, making them suitable for compact devices with limited space.
- LFP vs. Lead-Acid Batteries:
- Durability: LFP batteries outshine lead-acid in cycle life, enduring more charge-discharge cycles without significant performance degradation.
- Specific Energy: Lead-acid batteries are cost-effective but have lower specific energy compared to both LFP and Li-ion technologies.
- LFP vs. Nickel-Based Chemistries:
- Thermal Stability: LFP batteries exhibit better thermal stability than nickel-based chemistries, which can suffer from poor thermal characteristics.
- Specific Energy: Nickel-based chemistries offer high specific energy but may come with compromises in safety.
Each battery type has its strengths and weaknesses, and the choice depends on specific application requirements. Consider factors like safety, energy density, cycle life, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact when selecting the most suitable battery for your needs.
How LFP Batteries Are Made
Ever wondered how Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries, known for their stellar performance and safety, are made? Let’s break down the key steps in their production:

- Cathode Preparation:
- Lithium iron phosphate powder, mixed with a conductive additive, forms the cathode material.
- This mixture is coated onto aluminum foil, creating the cathode electrode.
- Anode Material Creation:
- The anode material, usually graphite or carbon-based, is prepared by coating copper foil with a slurry containing the active material and a binder.
- The resulting mixture forms the anode electrode.
- Assembly and Sealing:
- Assembling both electrodes with a separator in between prevents short circuits.
- The electrodes and separator are rolled into a cylindrical shape or stacked for prismatic cells.
- Electrolyte is added to aid ion movement during charging and discharging, and the battery cell is sealed to ensure it remains leak-proof.
While specific manufacturing processes may vary among manufacturers, these fundamental steps offer insight into the creation of LFP batteries.
The Future of LFP Technology
Curious about the future of Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries? Let’s explore the exciting prospects that lie ahead for this technology:
- Renewable Energy Storage:
- LFP batteries are poised to play a crucial role in storing excess energy from renewable sources like solar and wind power.
- With high energy density, long cycle life, and excellent thermal stability, LFP batteries are ideal for meeting the increasing demand for reliable energy storage in sustainable initiatives.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs):
- The inherent safety features of LFP batteries position them as a promising choice for the growing electric vehicle market.
- Governments promoting EV adoption find LFP batteries appealing due to their reduced risk of overheating or fire hazards compared to other lithium-ion types.
- Advancements and Research:
- Ongoing research focuses on improving the performance and cost-effectiveness of LFP batteries through innovations in manufacturing processes.
- Nanostructuring electrodes and exploring new materials aim to enhance energy density while maintaining safety characteristics.
- Consumer Electronics:
- The scalability of LFP technology makes it well-suited for meeting the demand for longer battery life in portable electronic devices.
- From smartphones to laptops, LFP batteries provide a reliable and safe power source for consumer electronics.
- Addressing Energy Density Challenges:
- While energy density improvements are underway, ongoing research, including hybridization with other materials, aims to boost capacity without compromising safety or reliability.
In conclusion, the future of LFP technology holds immense potential, impacting diverse sectors with continuous advancements and a focus on meeting evolving energy storage needs.
FAQs
What are the raw materials for LFP battery?
-
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4): The key raw material for LFP batteries is lithium iron phosphate, which serves as the cathode material. This compound contributes to the high energy density and stability of LFP batteries, making them suitable for various applications.
-
Conductive Agent and Binder: Along with lithium iron phosphate, LFP battery production involves the use of a conductive agent and a binder. The conductive agent facilitates the movement of electrons within the battery, enhancing its overall performance. The binder helps hold the active materials together, ensuring the structural integrity of the battery.
-
Advantages of LFP Batteries: LFP batteries offer several advantages, including high energy density, long cycle life, and safety. They are widely used in electric vehicles, energy storage systems, and other fields due to their reliability, environmental friendliness, and ability to withstand high temperatures.
What are the disadvantages of LiFePO4?
-
Higher Cost: LiFePO4 batteries are generally more expensive than other types of batteries. This is primarily due to the high-quality materials and complex manufacturing processes involved in their production. However, their long lifespan and performance advantages can offset the initial cost.
-
Lower Nominal Voltage per Cell: LiFePO4 batteries have a lower nominal voltage per cell compared to lithium-ion batteries. This means they store less energy per cell, resulting in reduced energy density. It is important to consider the impact of lower energy density on device performance and efficiency when choosing LiFePO4 batteries.
-
Lower Energy Density: LiFePO4 batteries have lower energy densities compared to lithium-ion batteries. This means they store less power in the same amount of space, resulting in reduced capacity. While this might limit their potential in certain applications, LiFePO4 batteries still offer advantages such as longer lifespan and improved safety.
How to make LFP batteries?
-
Preparation of Cathode and Anode Materials: The manufacturing process begins with the preparation of cathode and anode materials. The cathode material, typically lithium iron phosphate, serves as a source of lithium ions, while the anode material, such as graphite or lithium titanate, allows reversible lithium-ion intercalation during battery operation.
-
Electrolyte Filling and Ion Transportation: The electrode and separator of the battery are filled with an electrolyte, which facilitates the transportation of positive lithium ions from the cathode to the anode. The electrolyte composition typically involves lithium salt in an organic solution, enabling the movement of lithium ions within the battery.
-
Battery Management System: To ensure the safe and efficient operation of LFP batteries, a battery management system is employed. This system monitors and maintains cell balancing, state of charge, depth of discharge, and state of health of the battery. It also protects against overcharging and deep discharging, enhancing the overall performance and lifespan of the battery.





