As the demand for efficient energy storage solutions continues to grow, understanding the differences between Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) and Ternary (NMC) lithium batteries is essential. Both technologies have unique advantages and applications, making them suitable for various uses. In this article, we will provide an in-depth comparison of LiFePO4 and NMC batteries, focusing on their performance, safety, lifecycle, and environmental impact.
Understanding LiFePO4 and NMC Batteries
LiFePO4 batteries utilize lithium iron phosphate as the cathode material, while NMC batteries use a combination of nickel, manganese, and cobalt. This fundamental difference in chemistry leads to variations in performance characteristics, safety profiles, and applications.
Performance Comparison
1. Energy Density
-
LiFePO4 Batteries: Typically have a lower energy density, ranging from 90 to 160 Wh/kg. While this may seem limiting, it provides a stable power output that is beneficial for applications requiring consistent energy delivery.
-
NMC Batteries: Offer higher energy densities, usually between 150 to 250 Wh/kg. This makes NMC batteries ideal for applications where weight and space are critical factors, such as in electric vehicles.
2. Discharge Rates
- LiFePO4 Batteries: Known for their excellent discharge rates, LiFePO4 batteries can handle high currents without significant voltage drop. This feature is particularly advantageous for applications requiring quick bursts of power.
- NMC Batteries: Also provide good discharge rates but can experience performance degradation under extreme conditions. They are generally optimized for applications that require sustained power rather than rapid bursts.
Safety Features
1. Thermal Stability
-
LiFePO4 Batteries: Renowned for their thermal stability, LiFePO4 batteries are less prone to thermal runaway—a condition where battery temperatures rise uncontrollably. This makes them inherently safer for various applications.
-
NMC Batteries: While NMC batteries have improved safety features compared to older lithium technologies, they still pose a risk of thermal runaway under certain conditions. Proper management systems are essential to mitigate these risks.
2. Chemical Composition
- LiFePO4 Batteries: Free from toxic heavy metals like cobalt, LiFePO4 batteries present fewer environmental hazards during production and disposal.
- NMC Batteries: The presence of cobalt raises ethical concerns regarding sourcing and environmental impact. As demand for cobalt increases, so do concerns about its availability and ecological footprint.
Lifecycle and Durability
1. Cycle Life
-
LiFePO4 Batteries: Typically offer a longer cycle life of about 3,000 to 5,000 cycles, making them a cost-effective choice over time. Their ability to withstand deep discharges without significant capacity loss contributes to their longevity.
-
NMC Batteries: Generally provide a cycle life of around 1,500 to 3,000 cycles. While this is sufficient for many applications, it may not match the durability offered by LiFePO4 technology.
2. Maintenance Requirements
- LiFePO4 Batteries: Require minimal maintenance due to their robust design and chemistry. Users can expect lower operational costs over the battery’s lifespan.
- NMC Batteries: May require more careful monitoring and management systems to ensure optimal performance and safety, particularly in high-demand applications.
Environmental Impact
1. Recycling and Disposal
-
LiFePO4 Batteries: Easier to recycle due to their non-toxic composition. The absence of heavy metals simplifies the recycling process and reduces environmental hazards.
-
NMC Batteries: Recycling can be more complicated due to the presence of cobalt and other metals. However, advancements in recycling technologies are improving the efficiency of processing NMC batteries.
2. Sustainability Concerns
- LiFePO4 Batteries: Considered more sustainable due to their lower environmental impact during production and disposal.
- NMC Batteries: The reliance on cobalt raises sustainability concerns as mining practices can lead to environmental degradation and human rights issues.
Latest Developments in Battery Technology
Recent advancements in battery technology have focused on enhancing both LiFePO4 and NMC chemistries:
- Innovations in battery management systems (BMS) are improving safety features across both types.
- Research into alternative materials aims to reduce reliance on cobalt in NMC batteries while enhancing energy density in LiFePO4 options.
Data Chart Comparison: LiFePO4 vs NMC Batteries
| Feature | LiFePO4 Battery | NMC Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | 90 – 160 Wh/kg | 150 – 250 Wh/kg |
| Cycle Life | 3,000 – 5,000 cycles | 1,500 – 3,000 cycles |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent | Moderate |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Requires monitoring |
| Environmental Impact | Non-toxic & easier to recycle | Contains cobalt; recycling complex |
FAQs About LiFePO4 and NMC Batteries
What applications are best suited for LiFePO4 batteries?
LiFePO4 batteries are ideal for stationary energy storage systems, electric vehicles requiring safety and longevity, and applications where consistent power delivery is essential.
How do I know which battery type is right for my needs?
Consider factors such as energy density requirements, cycle life expectations, safety concerns, and environmental impact when choosing between LiFePO4 and NMC batteries.
Are there any new technologies being developed for these battery types?
Yes, ongoing research aims to enhance both chemistries by improving energy density in LiFePO4 batteries and reducing cobalt dependency in NMC batteries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both LiFePO4 and NMC batteries offer unique advantages that cater to different needs within the energy storage market. While LiFePO4 excels in safety, lifecycle longevity, and environmental impact, NMC provides higher energy density suited for weight-sensitive applications like electric vehicles. Understanding these differences allows consumers and businesses alike to make informed decisions tailored to their specific requirements.For customized lithium solutions tailored specifically to your needs—whether for electric vehicles or renewable energy systems—contact Redway Battery today for a quick quote!
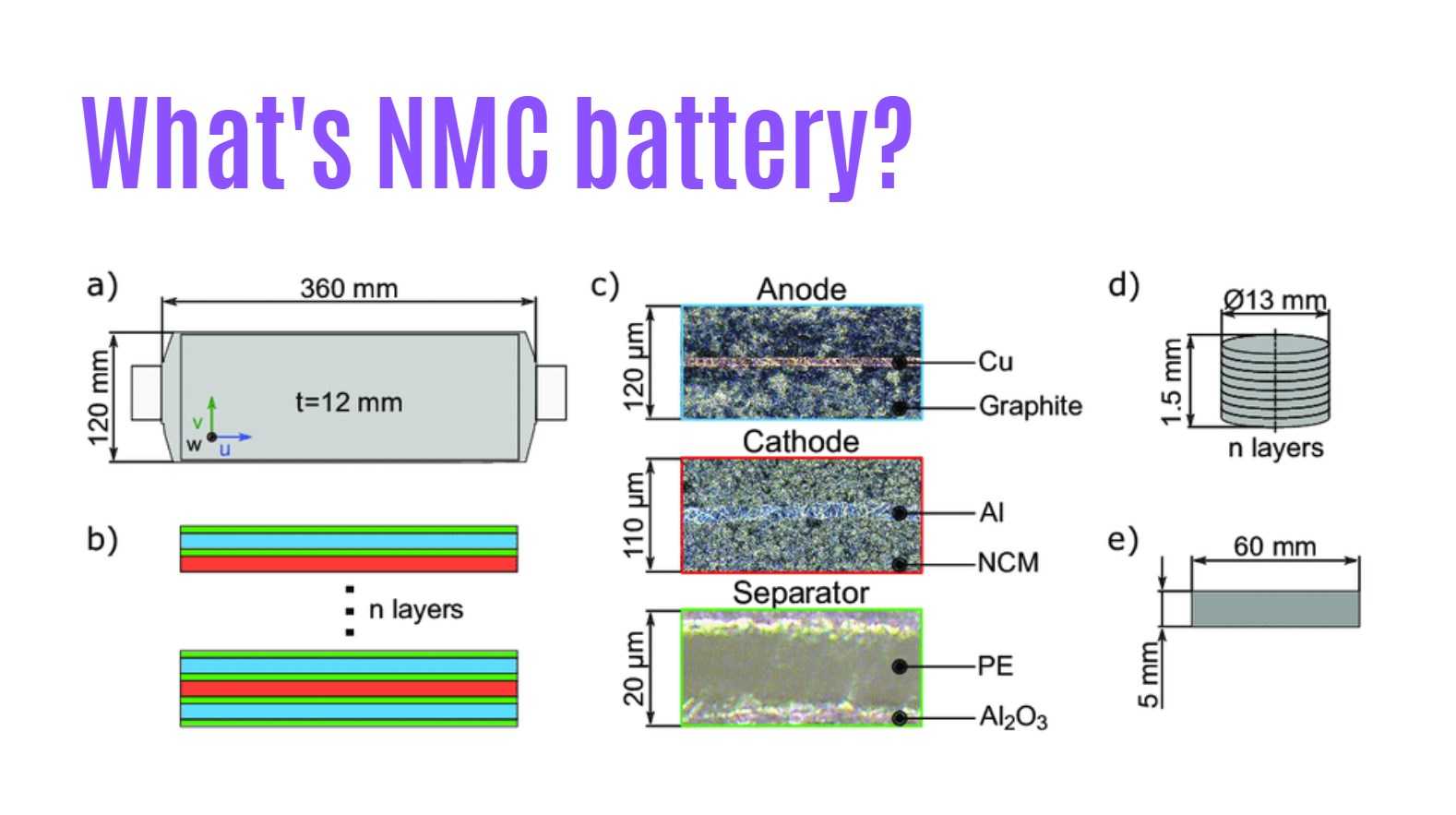
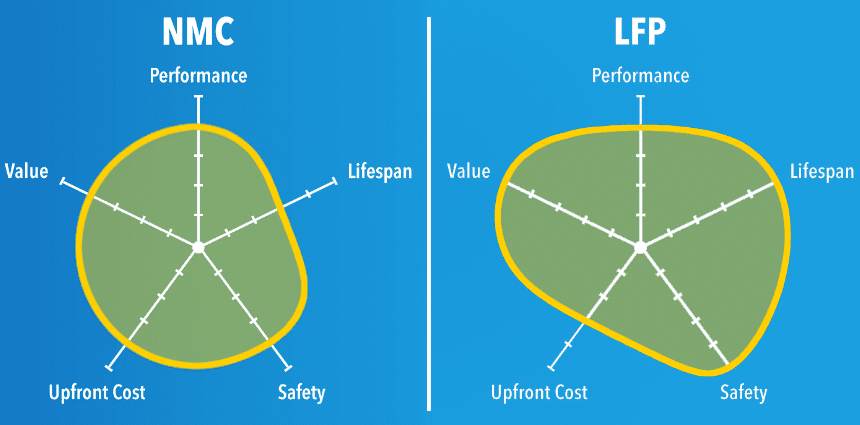

FAQs
Why LiFePO4 Batteries Outperform NMC in Safety and Longevity
-
Stability and Reduced Risk of Thermal Runaway:
LiFePO4 batteries have a stable chemistry that significantly reduces the risk of thermal runaway. Thermal runaway is a hazardous condition where internal battery heat rapidly increases, leading to destabilization and accelerated degradation. The stable chemistry of LiFePO4 batteries ensures a more controlled and safer operation, contributing to their longer lifespan. -
Longer Lifespan Confirmed by Independent Tests:
Independent degradation tests have demonstrated that LiFePO4 batteries have a longer life span compared to NMC batteries. These tests provide empirical evidence supporting the superior longevity of LiFePO4 batteries. The longer lifespan of LiFePO4 batteries makes them a reliable choice for applications that require extended battery life and durability. -
Safer Chemistry:
LiFePO4 batteries are considered safer than NMC batteries due to their specific chemical composition. At higher temperatures, the lithium iron phosphate alloy in LiFePO4 batteries is more stable compared to the nickel manganese cobalt composition in NMC batteries. This enhanced stability contributes to a reduced risk of thermal runaway and improves the overall safety of LiFePO4 batteries.
How NMC Batteries Excel in Energy Density and Power Output

Why Choosing the Right Lithium Battery Chemistry Matters
-
Performance and Efficiency: Different lithium battery chemistries offer varying levels of performance and efficiency. For example, lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries are known for their high performance, low resistance, and longer cycle life. This makes them ideal for applications that require consistent power output and extended battery life.
-
Safety and Reliability: Battery safety is a top priority, especially in applications such as electric vehicles and energy storage systems. Choosing the right lithium battery chemistry, such as LiFePO4, can provide enhanced safety features, including greater thermal stability and reduced risk of thermal runaway. This ensures safe and reliable operation, even in demanding conditions.
-
Application-Specific Requirements: Different applications have specific requirements when it comes to battery chemistry. For example, electric vehicles require batteries with high energy density and fast charging capabilities, while renewable energy storage systems prioritize long cycle life and deep discharge capabilities. By understanding the unique requirements of your application, you can choose the lithium battery chemistry that best meets your needs.
How Battery Safety Differs NMC vs LiFePO4 Nail Test
When comparing the safety of NMC and LiFePO4 batteries using the nail penetration test, it is evident that NMC batteries exhibit lower internal short circuit tolerance, making them more susceptible to short circuits when penetrated by a nail. In contrast, LiFePO4 batteries demonstrate superior safety and higher tolerance to nail penetration. This makes LiFePO4 batteries a safer choice for applications where battery safety is a critical concern.
-
Nail Penetration Test Results:
Through the nail penetration test, it has been observed that NMC batteries exhibit lower internal short circuit tolerance compared to LiFePO4 batteries. This means that NMC batteries are more susceptible to internal short circuits when subjected to nail penetration. -
Safety Implications:
The lower internal short circuit tolerance of NMC batteries can pose safety concerns, as it increases the risk of short circuits and potential accidents. On the other hand, LiFePO4 batteries demonstrate better safety performance and higher tolerance to nail penetration, making them a safer choice for various applications. -
Importance of Choosing the Right Battery Chemistry:
The differences in safety between NMC and LiFePO4 batteries highlight the significance of selecting the appropriate battery chemistry for specific applications. By understanding the safety characteristics of different lithium battery chemistries, we can make informed decisions to ensure safer and more reliable energy storage solutions.
More FAQs
Is LiFePO4 better than NMC? The superiority of LiFePO4 (LFP) or NMC (Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide) batteries depends on specific application requirements. LFP batteries are known for their safety and longevity, while NMC batteries offer higher energy density and better overall performance in terms of power output.
Which is better, NMC or LFP batteries? It depends on the application. NMC batteries generally have higher energy density and better power output, making them suitable for electric vehicles and high-performance devices. On the other hand, LFP batteries are known for their safety, longevity, and resistance to thermal runaway, making them ideal for stationary energy storage and applications where safety is paramount.
What battery is better than LiFePO4? There isn’t a straightforward answer, as it depends on the specific requirements of the application. NMC batteries are often considered a viable alternative to LiFePO4 batteries due to their higher energy density and performance characteristics.
What is the voltage difference between NMC and LiFePO4? The voltage difference between NMC and LiFePO4 batteries is typically minimal. Both types of batteries generally have similar nominal voltages, typically around 3.2 to 3.7 volts per cell.
What are the disadvantages of LiFePO4? Some disadvantages of LiFePO4 batteries include lower energy density compared to other lithium-ion chemistries like NMC, which results in larger and heavier battery packs for the same energy storage capacity. Additionally, they tend to have lower specific power and voltage compared to NMC batteries.
Does Tesla use NMC batteries? Yes, Tesla uses NMC battery cells in some of its electric vehicle models, particularly those with higher energy density requirements.
Why is NMC more expensive than LFP? NMC batteries are more expensive than LFP batteries due to their higher energy density and more complex manufacturing process. Additionally, the materials used in NMC batteries, such as cobalt, can be more costly and subject to price fluctuations.
Why NMC is better than LFP? NMC batteries are often considered better than LFP batteries for applications requiring higher energy density and power output. They also tend to have better cycle life and faster charging capabilities.
Is NMC safer than LFP? No, LiFePO4 batteries are generally considered safer than NMC batteries due to their inherent thermal stability and resistance to thermal runaway. NMC batteries, while offering higher energy density, are more prone to safety risks under certain conditions.
What is the disadvantage of NMC? One disadvantage of NMC batteries is their reduced safety compared to LiFePO4 batteries. NMC batteries are more prone to thermal runaway and have a higher risk of catching fire or exploding under certain conditions.
Do LFP batteries last longer than NMC? LiFePO4 batteries tend to have longer cycle life and better calendar life compared to NMC batteries, making them suitable for applications where longevity and reliability are essential.

Why is Tesla switching to LFP? Tesla is switching to LFP batteries for some models due to their lower cost, improved safety, and suitability for stationary energy storage applications, such as grid storage and home energy systems.
What is the life of a lithium NMC battery? The lifespan of a lithium NMC battery can vary depending on factors such as usage, charging habits, and environmental conditions. Generally, well-maintained NMC batteries can last several hundred charge-discharge cycles or more.
How much does LFP cost vs NMC? The cost of LFP batteries may be lower than NMC batteries due to factors such as simpler manufacturing processes and lower material costs. However, prices can vary depending on factors such as brand, capacity, and market conditions.